COC(Clash of Clans) is a freemium mobile MMO strategy video game developed and published by Supercell.The game was released for iOS platforms on 2 August, 2012,[1] and on Google Play for Android on 7 October, 2013 (from wiki)
The answer is 2D game,actually we should call 2.5D. 第一眼看到COC里面的所有动画人物给人的感觉都是3D的,但后来知道了Isometric Tileset Engine的概念。
Isometric Tileset Engine
What is Isometric Tileset Engine?
(斜视角游戏的地图渲染) (Isometric Tiles Introduction) 结合上述文章,我们可以知道,Isometric Tileset Engine主要是通过美术制作出Isometric Projection(we angle our camera along two axes (swing the camera 45 degrees to one side, then 30 degrees down))的2D图片来实现游戏的3D效果(2.5D)。
What does game with isometric projection look like?
典型的Isometric Projection游戏有: Age of Empires Diablo 2
UI的Render Mode主要分为三种 2.1 Screen Space – Overlay(Rendered on top of the secene) 2.2 Screen Space – Camera(有距离感的UI,受摄像机设置影响) 2.3 World Space(3D UI,有深度概念,会被3D物体遮挡)
voidStart() { mBBulletsList = new List<GameObject>(); mSBulletsList = new List<GameObject>();
for (int i = 0; i < mBBulletPoolAmount; i++) { GameObject bbulletobj = Instantiate(mBuildingBullet) as GameObject; bbulletobj.SetActive(false); mBBulletsList.Add(bbulletobj); }
for (int j = 0; j < mSBulletPoolAmount; j++) { GameObject sbulletobj = Instantiate(mSoldierBullet) as GameObject; sbulletobj.SetActive(false); mSBulletsList.Add(sbulletobj); } }
public GameObject GetBuildingBulletObject() { for (int i = 0; i < mBBulletsList.Count; i++) { if (!mBBulletsList[i].activeInHierarchy) { mBBulletsList[i].SetActive(true); return mBBulletsList[i]; } }
if (mWillGrow) { GameObject bbulletobj = Instantiate(mBuildingBullet) as GameObject; mBBulletsList.Add(bbulletobj); return bbulletobj; }
returnnull; }
public GameObject GetSoldierBulletObject() { for (int i = 0; i < mSBulletsList.Count; i++) { if (!mSBulletsList[i].activeInHierarchy) { mSBulletsList[i].SetActive(true); return mSBulletsList[i]; } }
if (mWillGrow) { GameObject sbulletobj = Instantiate(mSoldierBullet) as GameObject; mSBulletsList.Add(sbulletobj); return sbulletobj; }
[Serializable] publicclassSoldier : MonoBehaviour, GameObjectType { public SoldierState SCurrentState { set { if (mSCurrentState != null) { mSCurrentState.ExitState(); } mSCurrentState = value; mSCurrentState.EnterState(); } } [HideInInspector] private SoldierState mSCurrentState;
[HideInInspector] public SoldierAttackState mSAttackState;
[HideInInspector] public SoldierDeadState mSDeadState;
[HideInInspector] public SoldierMoveState mSMoveState;
......
publicvirtualvoidAwake() { mSAttackState = new SoldierAttackState(this);
mSMoveState = new SoldierMoveState(this);
mSDeadState = new SoldierDeadState(this);
...... }
publicvirtualvoidUpdate() { if (gameObject) { mSCurrentState.UpdateState(); } }
...... }
Decision Trees(决策树 – 用于简单的AI(Decision making)) Decision Trees主要用于AI体做决策,通过对已知数据的分析判断,根据Decision Tree抉择出最终的决定(即AI行为)。(项目里我主要使用FSM而非Decision Trees) 下图来源:《Artificial Intelligence for Game》 – Ian Millington
A Star(A Star是 Dijkstra(著名的最短路径算法)基础上通过一个启发因子来预估给定节点到目标节点的距离来使得路径节点搜索是向目标节点方向逼近不至于出现搜索大量无效节点的情况) (AI相关学习)
A Star
Searching
通过搜索,我发现网络上有现成的很完善的A Star的版本 A Star Pathfinding Project(Asset) 但通过使用后发现,里面所支持的Four,Six and Eight connections都不符合我的需求(每个点都和周围的八个点连通),所以最终放弃了A Star Pathfinding Project而决定自己实现自己的A Star Pathfinding
Create Myself A Star
A Star Preperation
结合Artificial-Inteligence-Study的学习,让我们了解下A Star里的一些基本概念和核心思想: A Star属于什么图? A Star里的图属于导航图(Navigation Graph),是基于开销的图搜索(cost-based graph searches)
Dijstra算法改进: A Star – 和Dijkstra算法的唯一区别是对搜索边界上的点的开销(GCost)的计算。因为Dijstra的搜索扩展方向是由GCost决定的,所以A Star算法通过给GCost添加一个启发因子(H)来确保搜索行进方向。 F的计算: F = G + H G是到达一个节点的累计开销, H是一个启发因子,它给出的是节点到目标节点的估计距离。
using UnityEngine; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System; using UnityEngine.Assertions;
publicclassSearchAStar { publicstruct PathInfo {
public List<int> PathToTarget { get { return mPathToTarget; } set { mPathToTarget = value; } } private List<int> mPathToTarget;
public List<Vector3> MovementPathToTarget { get { return mMovementPathToTarget; } set { mMovementPathToTarget = value; } } private List<Vector3> mMovementPathToTarget;
publicbool IsWallInPathToTarget { get { return mIsWallInPathToTarget; } set { mIsWallInPathToTarget = value; } } privatebool mIsWallInPathToTarget;
publicint WallInPathToTargetIndex { get { return mWallInPathToTargetIndex; } set { mWallInPathToTargetIndex = value; } } privateint mWallInPathToTargetIndex;
publicfloat CostToTarget { get { return mCostToTarget; } set { mCostToTarget = value; } } privatefloat mCostToTarget;
publicint ITarget { set { mITarget = value; } get { return mITarget; } } privateint mITarget;
publicint OriginalTarget { get { return mOriginalTarget; } set { mOriginalTarget = value; } } privateint mOriginalTarget;
publicint NodesSearched { get { return mNodesSearched; } set { mNodesSearched = value; } } privateint mNodesSearched;
publicint EdgesSearched { get { return mEdgesSearched; } set { mEdgesSearched = value; } } privateint mEdgesSearched;
//this list of edges is used to store any subtree returned from any of the graph algorithms /* public List<GraphEdge> SubTree { get { return mSubTree; } set { mSubTree = value; } } private List<GraphEdge> mSubTree; */ /* public PathInfo() { ResetPathInfo(); } */
public PathInfo DeepCopy() { PathInfo pi = (PathInfo)this.MemberwiseClone(); pi.PathToTarget = new List<int>(mPathToTarget); pi.MovementPathToTarget = new List<Vector3>(mMovementPathToTarget);
if (!mIsIgnoreWall) { //No matter the wall in path is jumpable or not, we should record it as useful information if (mGraph.Nodes[nd].IsWall /*&& !mGraph.Nodes[nd].IsJumpable*/) { mAStarPathInfo.IsWallInPathToTarget = true; mAStarPathInfo.WallInPathToTargetIndex = nd; } }
while (!mPQ.Empty()) { //Get lowest cost node from the queue int nextclosestnode = mPQ.Pop().Key;
mAStarPathInfo.NodesSearched++;
//move this node from the frontier to the spanning tree if (mSearchFrontier[nextclosestnode] != null && mSearchFrontier[nextclosestnode].IsValidEdge()) { mShortestPathTree[nextclosestnode] = mSearchFrontier[nextclosestnode]; } //If the target has been found exit if (nextclosestnode == mITarget) { return; }
//Now to test all the edges attached to this node List<GraphEdge> edgelist = mGraph.EdgesList[nextclosestnode]; GraphEdge edge; for (int i = 0; i < edgelist.Count; i++) { edge = edgelist[i]; //calculate the heuristic cost from this node to the target (H) float hcost = Heuristic_Euclid.Calculate(mGraph, mITarget, edge.To) * mHCostPercentage;
//calculate the 'real' cost to this node from the source (G) float gcost = mGCosts[nextclosestnode] + edge.Cost;
//if the node has not been added to the frontier, add it and update the G and F costs if (mSearchFrontier[edge.To] != null && !mSearchFrontier[edge.To].IsValidEdge()) { mFCosts[edge.To].Value = gcost + hcost; mGCosts[edge.To] = gcost;
mPQ.Push(mFCosts[edge.To]);
mSearchFrontier[edge.To] = edge;
mAStarPathInfo.EdgesSearched++;
if (mBDrawExplorePath) { Debug.DrawLine(mGraph.Nodes[edge.From].Position, mGraph.Nodes[edge.To].Position, Color.yellow, mExplorePathRemainTime); } }
//if this node is already on the frontier but the cost to get here //is cheaper than has been found previously, update the node //cost and frontier accordingly elseif (gcost < mGCosts[edge.To]) { mFCosts[edge.To].Value = gcost + hcost; mGCosts[edge.To] = gcost;
//Due to some node's f cost has been changed //we should reoder the priority queue to make sure we pop up the lowest fcost node first //compare the fcost will make sure we search the path in the right direction //h cost is the key to search in the right direction mPQ.ChangePriority(edge.To);
while (!mPQ.Empty()) { //Get lowest cost node from the queue int nextclosestnode = mPQ.Pop().Key;
mAStarPathInfo.NodesSearched++;
//move this node from the frontier to the spanning tree if (mSearchFrontier[nextclosestnode] != null && mSearchFrontier[nextclosestnode].IsValidEdge()) { mShortestPathTree[nextclosestnode] = mSearchFrontier[nextclosestnode]; }
//Now to test all the edges attached to this node List<GraphEdge> edgelist = mGraph.EdgesList[nextclosestnode]; GraphEdge edge; for (int i = 0; i < edgelist.Count; i++) { edge = edgelist[i]; //calculate the heuristic cost from this node to the target (H) float hcost = Heuristic_Euclid.Calculate(mGraph, mITarget, edge.To) * mHCostPercentage;
//calculate the 'real' cost to this node from the source (G) float gcost = mGCosts[nextclosestnode] + edge.Cost;
//if the node has not been added to the frontier, add it and update the G and F costs if (mSearchFrontier[edge.To] != null && !mSearchFrontier[edge.To].IsValidEdge()) { mFCosts[edge.To].Value = gcost + hcost; mGCosts[edge.To] = gcost;
mPQ.Push(mFCosts[edge.To]);
mSearchFrontier[edge.To] = edge;
mAStarPathInfo.EdgesSearched++;
if (mBDrawExplorePath) { Debug.DrawLine(mGraph.Nodes[edge.From].Position, mGraph.Nodes[edge.To].Position, Color.yellow, mExplorePathRemainTime); } }
//if this node is already on the frontier but the cost to get here //is cheaper than has been found previously, update the node //cost and frontier accordingly elseif (gcost < mGCosts[edge.To]) { mFCosts[edge.To].Value = gcost + hcost; mGCosts[edge.To] = gcost;
//Due to some node's f cost has been changed //we should reoder the priority queue to make sure we pop up the lowest fcost node first //compare the fcost will make sure we search the path in the right direction //h cost is the key to search in the right direction mPQ.ChangePriority(edge.To);
mSearchFrontier[edge.To] = edge;
mAStarPathInfo.EdgesSearched++; } } } }
//The A* search algorithm with strickdistance with wall consideration privatevoidSearch(float strickdistance, bool isignorewall) { float currentnodetotargetdistance = Mathf.Infinity;
mPQ.Clear();
mPQ.Push(mFCosts[mISource]);
//mSearchFrontier [mISource] = new GraphEdge (mISource, mISource, 0.0f); mSearchFrontier[mISource].From = mISource; mSearchFrontier[mISource].To = mISource; mSearchFrontier[mISource].Cost = 0.0f; GraphEdge edge = new GraphEdge(); int nextclosestnode = -1;
while (!mPQ.Empty()) { //Get lowest cost node from the queue nextclosestnode = mPQ.Pop().Key;
mAStarPathInfo.NodesSearched++;
//move this node from the frontier to the spanning tree if (mSearchFrontier[nextclosestnode] != null && mSearchFrontier[nextclosestnode].IsValidEdge()) { mShortestPathTree[nextclosestnode] = mSearchFrontier[nextclosestnode]; }
//Now to test all the edges attached to this node List<GraphEdge> edgelist = mGraph.EdgesList[nextclosestnode]; for (int i = 0; i < edgelist.Count; i++) { //Avoid pass refrence edge.Reset(); edge.From = edgelist[i].From; edge.To = edgelist[i].To; edge.Cost = edgelist[i].Cost; //calculate the heuristic cost from this node to the target (H) float hcost = Heuristic_Euclid.Calculate(mGraph, mITarget, edge.To) * mHCostPercentage;
//calculate the 'real' cost to this node from the source (G) float gcost = 0.0f; if (isignorewall) { gcost = mGCosts[nextclosestnode] + edge.Cost;
if (mGraph.Nodes[edge.From].IsWall) { gcost -= mGraph.Nodes[edge.From].Weight; } if (mGraph.Nodes[edge.To].IsWall) { gcost -= mGraph.Nodes[edge.To].Weight; } } else { gcost = mGCosts[nextclosestnode] + edge.Cost; if (mGraph.Nodes[edge.From].IsJumpable) { gcost -= mGraph.Nodes[edge.From].Weight; } if (mGraph.Nodes[edge.To].IsJumpable) { gcost -= mGraph.Nodes[edge.To].Weight; } }
//if the node has not been added to the frontier, add it and update the G and F costs if (mSearchFrontier[edge.To] != null && !mSearchFrontier[edge.To].IsValidEdge()) { mFCosts[edge.To].Value = gcost + hcost; mGCosts[edge.To] = gcost;
mPQ.Push(mFCosts[edge.To]);
mSearchFrontier[edge.To].ValueCopy(edge);
mAStarPathInfo.EdgesSearched++;
if (mBDrawExplorePath) { Debug.DrawLine(mGraph.Nodes[edge.From].Position, mGraph.Nodes[edge.To].Position, Color.yellow, mExplorePathRemainTime); } }
//if this node is already on the frontier but the cost to get here //is cheaper than has been found previously, update the node //cost and frontier accordingly elseif (gcost < mGCosts[edge.To]) { mFCosts[edge.To].Value = gcost + hcost; mGCosts[edge.To] = gcost;
//Due to some node's f cost has been changed //we should reoder the priority queue to make sure we pop up the lowest fcost node first //compare the fcost will make sure we search the path in the right direction //h cost is the key to search in the right direction mPQ.ChangePriority(edge.To);
盲目搜索(Uniformed Graph Searches) (在搜索一个图时不考虑相关的边的开销) a. 深度优先搜索(DFS: Depth First Search) (搜索时尽可能地深入一个图。在搜索时,当它走入死胡同时,才会回溯,以回到上一个较浅的节点,在那里继续深度搜索) 注意: 使用Stack来模拟,先进后出(FILO)的原则 DFS优化: 一些图可能非常深,深度优先便可能非常容易地就在错误的路径上陷得很深,因而延误了搜索。 限制深度的搜索(Limited Search): 限制深度优先搜索算法在开始回溯之前可以进行多少步的深度搜索 缺点: 如何设置最大搜索深度 迭代加深深度优先搜索(Iterative Deepending Depth First Search) b. 广度优先搜索(BFS:Breadth First Search) (从源节点展开以检查从它出发的边指向的每一个节点,然后再从那些刚检查过的节点继续展开) 注意: 使用Queue来模拟,先进先出(FIFO)的原则 BFS缺点: 如果搜索的图非常大而且分支数很高,那么BFS就会浪费大量的内存并且表现出很低的效率。
基于开销的图搜索(cost-based graph searchs) a. 边放松(Edge Relaxation) (从源节点到抵达目标节点的路径上的所有其他节点中搜集当前最优路径(BPFSF: Best Path Found So Far)信息。这个信息在检查新的边时得到更新。如果刚检查的边表明,如果用通过此边到达一个节点的路径取代现有的最优路径会使路程更短,那么,这条边就 被加入,而路径也相应地更新) b. 最短路径树(SPT: Short Path Tree) (从任何节点到达源节点的最短路径) c. Dijkstra算法(Dijkstra Algorithm) (教授Edsger Wybe Dijkstra著名的寻找带全图的最短路径算法) 注意: 使用一个索引的优先队列(Indexed Priority Queue)来实现。 缺点: Dijkstra算法检查了太多的边。 d. Dijkstra算法的一个改进:A算法 (Dijkstra算法通过最小化开销进行搜索。在处理搜索边界上的点时,如果估计一下他们距离目标节点的开销,并将这个信息考虑进去,那么算法的效率就可以大大提高。这个估计值被称为启发因子。) 注意: A算法和Dijkstra算法的唯一区别是对搜索边界上的点的开销的计算。被修正的到节点的开销F用来决定节点在优先队列中的位置。 F的计算: F = G + H G是到达一个节点的累计开销, H是一个启发因子,它给出的是节点到目标节点的估计距离。 通过用这种方法使用一个启发因子,被修正的开销会指引搜索逼近目标节点,而不是在各个可能的方向发散的搜索。这也使需要检查的边更少。因此搜索的加速是Disjkstra算法和A算法的最主要区别。 A算法的实现需要维护两个用来存储开销的std::vector,一个用来保存每一个节点的F开销,作为优先队列的索引,另一个是每一个节点的G开销。
《Artificial Intelligence for Game》 – Ian Millington 1. Introduction 1.1 What is AI? Artificial intelligence is about making computers able to perform the thinking tasks that humans and animals are capable of
1.1.2 Game AI Pacman [Midway Games West, Inc, 1979] – state machine Warcraft –[Blizzard Entertainment, 1994] – Path finding
AI three basic needs: 1. Move Movement refers to algorithms that turn decisions into some kind of motion 2. Decision making Decision making involves a characterworking out what to do next 3. Strategy Strategy refers to an overall approach used by a group of characters – e.g. Harf-Life Note: Not all game applications require all levels of AI
1.2.5 Agent-Based AI Agent-based AI is about producing autonomous characters that take in information from the game data, determine what actions to take based on the information, and carry out those actions
1.3 Algorithms, Data Structures, and Representations 1.3.1 Algorithms
Tactical and Strategic AI 6.1 Waypoint Tactics 6.1.1 Tactical Locations
参考书籍: 《OpenGL Programming Guide 8th Edition》 – Addison Wesley 《Fundamentals of Computer Graphics (3rd Edition)》 – Peter Shirley, Steve Marschnner 《Real-Time Rendering, Third Edition》 – Tomas Akenine-Moller, Eric Haines, Naty Hoffman
Rendering Knowledge
在进入书籍内容的学习之前,先了解一些必要的知识
What is Rendering?
“Rendering is a process that takes as its input a set of objects and produces as its output an array of pixels.” – 《Fundamentals of Computer Graphics (3rd Edition)》
既然Rendering是通过处理一系列的对象数据最终输出成一组一组的像素呈现出来,那接下来的问题就是What is the rendering process(Graphic Pipeline)?
Application e.g collision detection, global acceleration algorithms, animation, physics simulation….. (On CPU) Acceleration algorithms, such as hierarchical view frustum culling, are also implemented in this stage. – 《Real-Time Rendering, Third Edition》 可以看出Application阶段主要是做一些非渲染相关的一些计算,但部分计算也可以帮助我们减少渲染数量提高渲染效率(比如:hierachical view frustum culling)
Geometry Deal with transforms, projection. Computes what is to be draw, how it should be drawn, and where it should be drawn (On GPU) e.g. model and view transform, vertex shading, projection, clipping, and screen mapping – 《Real-Time Rendering, Third Edition》 可以看出Geometry阶段主要是负责3D到2D Screen的顶点运算和顶点剔除
Rasterizer Conversion from two-dimensional vertices in screen space – each with a z-value (depth value), and various shading information associated with each vertex – into pixels on the screen (On GPU) – 《Real-Time Rendering, Third Edition》 可以看出Rasterizer阶段主要是负责2D Screen的顶点像素运算(包括Z-Buffer test, Color computation, Alpha test, Stencil buffer等)
Accumulation Buffer – Images can be accumulated using a set of operators. E,g, motion blur……
那么什么是Shader(着色器)?Shader(着色器)和GPU硬件的关系是怎样的了? “Shaders are programmed using C-like shading languages such as HLSL, Cg and GLSL. These are compiled to a machine-independent assembly language, also called the intermediate language(IL). This assembly language is converted to the actual machine language in a separate step, usually in the drivers. This arrangement allows compatibility across different hardware implementations.” – Real-Time Rendering, Third Edition》 GPU的像素着色器单元和顶点着色器单元就对应了Shader里面的Pixel Shader和Vertex Shader。由于像素在计算机都是以RGB三种颜色构成,加上Alpha总共4个通道,所以GPU的像素着色器单元和顶点着色器单元一开始就被设计成为同时具备4次运算能力的算数逻辑运算器(ALU)
从上面可以看出Shader是machine-independent的,因为事先被编译成了与机器无关的intermediate language(This intermediate language can be seen as defining a virtual machine, which is targeted by the shading language compiler – 《Real-Time Rendering, Third Edition》), 最后才会被机器转换成机器码来运行.
可编程Shading进化史可参考 3.3 The Evolution of Programmable Shading – 《Real-Time Rendering, Third Edition》
了解了计算机架构与Shader的关系,让我们来看看Common-shader core virtual machine architecture and register layout吧
Input Type
Uniform inputs With values that remain constant throughout a draw call(but can be changed between draw calls) – accessed via read-only constant registers or constant buffers
Varying inputs Which are different for each vertex or pixel processed by the shader – accessed via varying input registers
Shader Knowledge
Shader
Shader programs can be compiled offline before program load or during run time. As with any compiler, there are options for generating different output files and for using different optimization levels. A compiled shader is stored as a string of text, which is passed to the GPU via the driver.
OpenGL is an application programming interface – “API” for short – which is merely a software library for accessing features in graphics hardware.(访问图形硬件设备功能的API)
OpenGL is a “C” language library(OpenGL是一个C语言库)
History
It was first developed at Silicon Graphics Computer Systems with Version 1,0 released in July of 1994(wiki)
Vertex Shader Process the data associated with that vertex
Tessellation Shader Tessellation uses patchs to describe an object’s shape, and allows relatively simple collections of patch geometry to be tessellated to increase the number of geometric primitives providing better-looking models (eg: LOD)
Geometry Shader Allows additional processing of individual geometric primitives, including creating new ones, before rasterization
Primitive Assembly Organizes the vertices into their associated geometric primitives in preparation for clipping and rasterization
Clipping Clip the vertex and pixels are outside of the viewport – this operation is handled automatically by OpenGL
Rasterization Fragment generation. Pixels have a home in the framebuffer, while a fragment still can be rejected and never update its associated pixel location.
Fragment Shading Use a fragment shading to determine the fragment’s final color, and potentially its depth value
Per-Fragment Operations If a fragment successfully makes it through all of the enabled tests (eg: depth testing, stencil testing), it may be written directly to the framebuffer, updating the color of its pixel, or if blending is enabled, the fragment’s color will be combined with the pixel’s current color to generate a new color that is written into the framebuffer
Note: Fragment’s visibility is determined using depth testing and stencil testing Pixel data is usually stored in texture map for use with texture mapping, which allows any texture stage to look up data values from one or more texture maps.
GLSL - OpenGL Shading Language 也称作 GLslang,是一个以C语言为基础的高阶着色语言。它是由 OpenGL ARB 所建立,提供开发者对绘图管线更多的直接控制,而无需使用汇编语言或硬件规格语言。
编译和执行 GLSL 着色器不是独立的应用程式;其需要使用 OpenGL API 的应用程式。C、C++、C#、Delphi 和 Java 皆支援 OpenGL API,且支援 OpenGL 着色语言。 GLSL 着色器本身只是简单的字串集,这些字串集会传送到硬件厂商的驱动程式,并从程式内部的 OpenGL API 进入点编译。着色器可从程式内部或读入纯文字档来即时建立,但必须以字串形式传送到驱动程式。
工具 GLSL 着色器可以事先建立和测试,现有以下 GLSL 开发工具: RenderMonkey - 这个软件是由 ATI 制作的,提供界面用以建立、编译和除错 GLSL 着色器,和 DirectX 着色器一样。仅能在 Windows 平台上执行。 GLSLEditorSample - 在 Mac OS X 上,它是目前唯一可用的程式,其提供着色器的建立和编译,但不能除错。它是 cocoa 应用程式,仅能在 Mac OS X 上执行。 Lumina - Lumina 是新的 GLSL 开发工具。其使用 QT 界面,可以跨平台。
The color space in OpenGL
In OpenGL, colors are represented in what’s called the RGB color space
以下是一个材质库文件的基本结构:
newmtl mymtl_1
材质颜色光照定义
纹理贴图定义
反射贴图定义
……
注释:每个材质库可含多个材质定义,每个材质都有一个材质名。用newmtl mtlName来定义一个材质。对于每个材质,可定义它的颜色光照纹理反射等描述特征。主要的定义格式如下文所示:
////////////////////////////////////////////////
材质颜色光照
1。环境反射有以下三种描述格式,三者是互斥的,不能同时使用。
Ka r g b ——用RGB颜色值来表示,g和b两参数是可选的,如果只指定了r的值,则g和b的值都等于r的值。三个参数一般取值范围为0.0~1.0,在此范围外的值则相应的增加或减少反射率;
Ka spectral file.rfl factor ——用一个rfl文件来表示。factor是一个可选参数,表示.rfl文件中值的乘数,默认为1.0;
Ka xyz x y z ——用CIEXYZ值来表示,x,y,z是CIEXYZ颜色空间的各分量值。y和z两参数是可选的,如果只指定了x的值,则y和z的值都等于r的值。三个参数一般取值范围为0~1。
2。漫反射描述的三种格式:
Kd r g b
Kd spectral file.rfl factor
Kd xyz x y z
3。镜反射描述的三种格式:
Ks r g b
Ks spectral file.rfl factor
Ks xyz x y z
4。滤光透射率描述的三种格式:
Tf r g b
Tf spectral file.rfl factor
Tf xyz x y z
5。光照模型描述格式:
illum illum_#
指定材质的光照模型。illum后面可接0~10范围内的数字参数。各个参数代表的光照模
“OpenGL Execute Model: The model for interpretation of OpenGL commands is client-server. An application (the client) issues commands, which are interpreted and processed by OpenGL (the server). The server may or may not operate on the same computer as the client. In this sense, OpenGL is network-transparent. “
“client-server 模式: OpenGL 是一种 client-server 模式,当你的应用程序调用 OpenGL 函数时, 它将告诉OpenGL client, 然后 client 将渲染命令传送给 server. 这里client 和 server可能是不同的计算机,或是同一台计算机上的不同进程。一般来说 server 是在 GPU上处理的, 而 client 是在 CPU 上处理的,这样分担了 CPU 的负担, 同时高效利用了GPU.”
但如果Client和Server没在同一个机器上,我们就需要一种一种网络传输协议框架来实现他们之间的交流: X Window System
GLUT是由Mark J. Kilgard在Silicon Graphics工作时所写,此人同时也是OpenGL Programming for the X Window System以及The Cg Tutorial: The Definitive Guide to Programmable Real-Time Graphics两书的作者。
Glew ( OpenGL Extension Wrangler Library) The OpenGL Extension Wrangler Library (GLEW) is a cross-platform C/C++ library that helps in querying and loading OpenGL extensions. GLEW provides efficient run-time mechanisms for determining which OpenGL extensions are supported on the target platform. All OpenGL extensions are exposed in a single header file, which is machine-generated from the official extension list.(Glew是一个支持跨平台的C/C++库,用于运行时鉴别OpenGL扩展所支持的版本) more info for extention tools
How to use Glu & Glew?
add glu.lib & glew.lib into additional dependencies
add the directory that includes glu.h & glew.h into include dirctory
Include GL/freeglut.h & GL/glew.h in source file Note: if you use static link, #define FREEGLUT_STATIC before you include GL/freeglut.h, otherwise it will look for freeglut.lib. #define GLEW_STATIC for Glew.
include GL/glew.h before GL/freeglut.h, otherwise, it will through “fatal error C1189: #error : gl.h included before glew.h”
V’ = V × M(m-w) × M(w-v) × M(v-p) 我们知道了M(m-w)是如何计算出来的了,接下来我们要了解M(w-v) – 世界坐标系到观察坐标系 在了解如何从世界坐标系转换到观察坐标系之前我们先来看看摄像机的定义: 位置 – (x,y,z) N – The vector from the camera to its target.(look at 朝向) V – When standing upright this is the vector from your head to the sky.(垂直于N向上的向量) U – This vector points from the camera to its “right” side”.(在N和V定了之后可以算出Camera的向右的向量)
后来看了《Mathematics for 3D Game Programming and Computer Grahpics 3rd section》的5.4.1 Depth Interpolation后明白了,光栅化的时候对于深度的运算证明了是对Z的倒数进行插值来得到Z的值的。 所以上述公式是成立的。
“Textures are composed of texels, which often contain color values.”
“Textures are bound to the OpenGL context via texture units, which are represented as binding points named GL_TEXTURE0 through GL_TEXTUREi where i is one less than the number of texture units supported by the implementation.”
The textures are accessed via sampler variables which were declared with dimensionality that matches the texture in shader
在真正接触Texutre之前,让我们理解下下列几个重要的概念:
Texture object – contains the data of the texture image itself, i.e. the texels(可以看出Texture object才是含有原始数据信息的对象)
Texture unit – texture object bind to a ‘texture unit’ whose index is passed to the shader. So the shader reaches the texture object by going through the texture unit.(我们访问texture数据信息并不是通过texture object,而是在shader里通过访问特定索引的texture unit去访问texture object里的数据)
Sampler Object – configure it with a sampling state and bind it to the texture unit. When you do that the sampler object will override any sampling state defined in the texture object.(Sampler Object一些sampling的配置信息,当用于texture object时会覆盖texture object里的原始sampler设定)
Sampler uniform – corresponding to handle of texture unit(用于在Shader里访问texture unit,texture unit和texture object绑定,也就间接的访问了texture的原始数据)
Relationship between texture object, texture unit, sampler object and sampler uniform
Create a texture object and load texel data into it glGenTextures() – gen texture object glBindTexture() – Tells OpenGL the texture object we refer to in all the following texture related calls, until a new texture object is bound. glTexImage2D() – load texel data into texture object
Associate a texture sampler with each texture map you intend to use in your shader glTexParameterf() – Texture采样方式的配置 还记得我们之前讲到的Sampler object吗?这里的配置就好比我们在sampler object里配置后再作用于特定的texture object 这里我就不说关于采样方式配置相关的内容了(采样方式会决定最终像素的计算方式),这里值得一提的是mipmap的概念。 mipmap主要是由于物体在场景中因为距离的缘故会在屏幕显示的大小有变化,如果我们在物体很远,只需要显示很小一块的时候还依然采用很大的纹理贴图,最终显示在屏幕上的纹理会很不清晰(失真)。为了解决这个问题,mipmap应运而生,通过事先生成或指定多个级别的同一纹理贴图,然后在程序运作的过程中通过计算算出应该使用哪一个等级的纹理贴图来避免大纹理小色块失真的问题。 我们可以手动通过: glTexStorage2D() && glTexSubImage2D() 去手动指定各级纹理贴图 也可以通过: glGenerateMipmap() – 自动去生成对应的mipmap纹理贴图 而程序在实际运作过程中如何去计算Mipmap Level这里就不做介绍了,详细参考《OpenGL Programming Guide 8th Edition》的Calculating the Mipmap章节 相关函数: textureLod() textureGrad()
Active texture unit and bind texture object to it glActiveTexture() – 激活特定的texture unit然后绑定特定texture object到特定texture unit上 glBindTexture() – 绑定特定的texture object到texture unit上
Retrieve the texel values through the texture sampler from your shader 首先我们在程序中指定了我们即将访问的Texture unit
Note: “The important thing to note here is that the actual index of the texture unit is used here, and not the OpenGL enum GL_TEXTURE0 (which has a different value).”
vsshader.vs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
#version 330
uniform mat4 gWVP;
layout (location = 0) in vec3 Position; layout (location = 1) in vec2 TexCoord;
Use immutable texture storage for textures wherever possible – When a texture is marked as immutable, the OpenGL implementation can make certain assumptions about the validity of a texture object (尽量使用不可变的texture storage, 这样OpenGL可以确保texture的有效性)
Create and initialize the mipmap chain for textures unless you have a good reason not to – improve the image quality of your program’s rendering, but also will make more efficient use of the caches in the graphics processor (为了渲染效率,减轻GPU负担,尽可能为texture创建mipmap)
Use an integer sampler in your shader when your texture data is an unnormalized integer and you intend to use the integer values it contains directly in the shader (尽量在shader里使用integer类型的sampler)
Note: “The maximum number of texture units supported by OpenGL can be determined by retrieving the value of the GL_MAX_COMBINED_ TEXTURE_IMAGE_UNITS constant, which is guaranteed to be at least 80 as of OpenGL 4.0.”
Proxy texture – used to test the capabilities of the OpenGL implementation when certain limits are used in combination with each other.
接下来我们看一下Spot Light: Spot Light和Point Light的主要区别在于,Spot Light定义了一个可影响的范围Cone和其垂直照射的方向。 而这个Cone通过Cutoff来定义: Cutoff – “ The cutoff value represents the maximum angle between the light direction and the light to pixel vector for pixels that are under the influence of the spot light.” 见下图:
More Advanced Lighting Model: Hemisphere Lighting: The idea behind hemisphere lighting is that we model the illumination as two hemispheres. The upper hemisphere represents the sky and the lower hemisphere represents the ground
Imaged-Based Lighting: “It is often easier and much more efficient to sample the lighting in such environments and store the results in one or more environment maps”
Lighting with Spherical Harmonics: “This method reproduces accurate diffuse reflection, based on the content of a light probe image, without accessing the light probe image at runtime”
接下来我们看一个真实渲染过程中比较重要的技术 – Shadow Mapping Shadow Mapping – Uses a depth texture to determine whether a point is lit or not.
Shadow mapping is a multipass technique that uses depth textures to provide a solution to rendering shadows (核心思想是通过比较通过光源点观察保存的深度信息(depth texture)和从观察点观察的深度信息来判断哪些点是shadowed,哪些是unshadowed – 注意比较的是通过映射到2D depth texture后的信息) A key pass is to view the scene from the shadow-casting light source rather than from the final viewpoint Two passes:
First Pass Shadow map – by rendering the scene’s depth from the point of the light into a depth texture, we can obtain a map of the shadowed and unshadowed points in the scene 在第一个pass中,我按照事例代码中写了,但发现最后显示的是纯白色的图像。 后来就不断去查问题。 首先,我怀疑depth texture是不是没有生成成功?
通过上图,我发现我自己的代码有三个Texture被生成,但Demo只有两个,并且我自己写的代码Enable的并非FBO 1绑定生成的Texture而是第三个Texture,所以这是我怀疑我在加载Mesh的时候加载了第三个Texture并将其绑定在了Texture unit 0,而我碰巧激活了这一个Texture unit。
// Load a white texture in case the model does not include its own texture if (!m_Textures[i]) { m_Textures[i] = newTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, "../Content/white.png");
Ret = m_Textures[i]->Load(); }
...... }
voidMesh::Render() { .....
if (MaterialIndex < m_Textures.size() && m_Textures[MaterialIndex]) { m_Textures[MaterialIndex]->Bind(GL_TEXTURE0); }
//Set uniform variable value glUniformMatrix4fv(gWVPLocation, 1, GL_TRUE, (const GLfloat*)p.GetWVPTrans());
gPTank->Render();
glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, 0); }
Second Pass Rendering the scene from the point of view of the viewer. Project the surface coordinates into the light’s reference frame and compare their depths to the depth recorded into the light’s depth texture. Fragments that are further from the light than the recorded depth value were not visible to the light, and hence in shadow
A skybox is a method of creating backgrounds to make a computer and video games level look bigger than it really is. When a skybox is used, the level is enclosed in a cuboid. (From wiki)
在OpenGL中实现Skybox是通过Cubemap。
In order to sample from the cubemap we will use a 3D texture coordinate instead of the 2D coordinate
Skydome – A skybox which uses a sphere is sometimes called a skydome.
Note: “An interesting performance tip is to always render the skybox last (after all the other models). The reason is that we know that it will always be behind the other objects in the scene.”
What is Normal Mapping? “Normal Mapping也叫做Dot3 Bump Mapping,它也是Bump Mapping的一种,区别在于Normal Mapping技术直接把Normal存到一张NormalMap里面,从NormalMap里面采回来的值就是Normal,不需要像HeightMap那样再经过额外的计算。”
Note: 在实际开发中我们并非一定要手动写代码运算,比如”Open Asset Import Library就支持flag called ‘aiProcess_CalcTangentSpace’ which does exactly that and calculates the tangent vectors for us”
Normal Map也通过工具可以生成,比如3D Max, Maya, 教程里用的GNU Image Manipulation Program (GIMP)…….
Parallax Mapping首先在一篇名为“Detailed Shape Representation with Parallax Mapping”的文章中提出。它的基本思想如下图示(本图来自Parallax Mapping with Offset Limiting: A PerPixel Approximation of Uneven Surfaces)。在图示的视线方向,如果表面是真正的凹凸不平的,如real surfacer所示,那么能看到的是B点,因此用于采样法线的正确纹理坐是TB而不是TA。 因此,我们需要对纹理坐标作偏移,为了满足实时渲染的要求,采用了取近似偏移的方法(如下图示),这种近似的算法已经可以达到比较好的效果。具体的offset计算可以参考:“Parallax Mapping with Offset Limiting: A PerPixel Approximation of Uneven Surface”,里面有详细的讲解。
Geometry shader(Optional) “The geometry shader sits logically right before primitive assembly and fragment shading.”
Receives as its input complete primitives as a collection of vertices, and these inputs are represented as array (Geometry shader接收完整图形的顶点集合,这些顶点集合在geometry shader中通过gl_in[]数组的方式访问)
gl_in的声明:
1 2 3 4 5
in gl_PerVertex { vec4 gl_Position; float gl_PointSize; float gl_ClipDistance[]; }gl_in[];
Geometry Features:
Producing Primitives They can have a different primitive type for their output than they do for their input. (EG: wireframe rendering, billboards and even interesting instancing effects)(Billboard效果见后面)
Culling Geometry Selective culling (geometry shader通过对特定的gl_PrimitiveIDIn进行生成特定的primitive实现selective culling) “gl_PrimitiveIDIn is a geometry language input variable that holds the number of primitives processed by the shader since the current set of rendering primitives was started.”
Geometry Amplification Produces more primitives on its output than it accepts on its input (can be used to implement fur shells or moderate tessellation – 因为可以对传入的primitive数据进行处理并生成多个primitive,所以能通过复制并改变primitive的信息数据来实现毛发等效果) Gl_MaxGeometryOutputVertices & glGetIntegerv(GL_MAX_GEOMETRY_OUTPUT_VERTICES) 毛发效果(来源OpenGL红宝书第八版):
Geometry Shader Instance Only runs the geometry shader and subsequent stages (rasterization) multiple times, rather than the whole pipeline (Geometry shader instancing draw call是通过运行多次geometry和rasterization和fragment来实现的) Geometry shader instancing is enabled in the shader by specifying the invocations layout qualifier
1 2
//gl_InvocationID identifies the invocation number assigned to the geometry shader invocation. layout (triangles, invocations = 4) in; //invocations = 4 indicates that the geometry shader will be called 4 times for each input primitives
Multiple Viewport Rendering gl_ViewportIndex (output variables available in the geometry shader that can redirect rendering into different regions of the framebuffer) gl_ViewportIndex is used to specify which set of viewport parameters will be used to perform the viewport transformation by OpenGL “ (Multiple viewport concept (多个视图窗口) – 这里主要是通过gl_ViewportIndex访问多个viewport,然后在geometry shader中通过指定primitive输出到特定的viewport来实现多个视图窗口) glViewportIndexedf() or glViewportIndexedfv() – specify how window x and y coordinates are generated from clip coordinates glDepthRangeIndexed() – specify how the window z coordinate is generated 效果展示(这里展示的OpenGL红宝书第八版的例子):
Layer Rendering It is also possible to use a 2D array texture as a color attachment and render into the slices of the array using a geometry shader (传入2D的纹理数组数据当做color attachment,通过geometry shader把传入的2D纹理数组信息去渲染多个slices) A restriction exits when using layered attachments to framebuffer: (使用layered attachment到framebuffer的规则): All the attachments of that framebuffer must be layered (framebuffer的所有attachment都必须是layered) Also, all attachments of a layered framebuffer must be of the same type (所有attach到layered framebuffer的attachment必须是同样类型) gl_Layer – built in variable in geometry shader – that is used to specify the zero-based index of the layer into which rendering will be directed 可实现的效果好比: Cube-Map 添加cube_map texture为color attachment到framebuffer中 cube-map texture(2D texture)这里会被划分成六个layer的array texture 通过instanced geometry shader生成六个faces(对应六个layer),通过gl_InvocationID和gl_Layer访问六个faces并做相应的projection matrices运算实现Cube_Map Face的效果
Advanced Transform Feedback 这里首先要了解下什么是Transform Feeback? Transform feedback can be considered a stage of the OpenGL pipeline that sits after all of the vertex-processing stages and directly before primitive assembly and rasterization. Transform feedback captures vertices as they are assembled into primitives and allow some or all of their attributes to be recorded into buffer objects. (Transform feedback发生在所有顶点运算阶段之后(所以如果geometry shader打开了,transform feedback就发生在geometry shader之后,相反是在vertex shader之后),在primitive assembly和光栅化之前。Transform feedback可以保存顶点的一些属性信息用于下一次的运算。)
Why do we need transform feedback? “DirectX10 introduced a new feature known as Stream Output that is very useful for implementing particle systems. OpenGL followed in version 3.0 with the same feature and named it Transform Feedback. The idea behind this feature is that we can connect a special type of buffer (called Transform Feedback Buffer right after the GS (or the VS if the GS is absent) and send our transformed primitives to it. In addition, we can decide whether the primitives will also continue on their regular route to the rasterizer. The same buffer can be connected as a vertex buffer in the next draw and provide the vertices that were output in the previous draw as input into the next draw. This loop enables the two steps above to take place entirely on the GPU with no application involvement (other than connecting the proper buffers for each draw and setting up some state).”
了解一些相关概念: Transform Feedback Objects: “The state required to represent transform feedback is encapsulated into a transform feedback object.”(transform feedback objects主要是存储跟transform feedback相关的一些状态。比如:哪一个buffer绑定到了transform feedback buffer的binding point)
因为粒子效果用到了Billboard来展示,所以在了解Particle System之前,我们先来看看Billboard是如何通过GS实现的: Billboard - “A billboard is a quad which always faces the camera. “
Before a geometry shader may be linked, the input primitive type, output primitive type, and the maximum number of vertices that is might produce must be specified (在链接geometry shader之前,我们必须先定义geometry shader的输入输出类型)
EmitVertex() - produces a new vertex at the output of the geometry shader. Each time it is called, a vertex is appended to the end of the current strip (将新的vertex加入到primitive的队列)
EndPrimitive() - breaks the current strip and signals OpenGL that a new strip should be started the next time EmitVertex() is called (将之前所加入的vertex算作一个primitive的信息,通知OpenGL开始下一个primitive的构造)
Note:
When the geometry shader exits, the current primitive is ended implicitly (如果geometry shader结束了,那么当前还没有调用EndPrimitive()的primitive将视作结束)
When EndPrimitive() is called, any incomplete primitives will simply be discarded (当EndPrimitive()被调用的时候,数据不完全的primitive将被抛弃 -- 不调用这个方法的primitive相当于culling掉)
boolParticleSystem::InitParticleSystem(const Vector3f& pos) { Particle Particles[MAX_PARTICLES]; ZERO_MEM(Particles); //Particle System最初的那个发射点信息 Particles[0].Type = PARTICLE_TYPE_LAUCHER; Particles[0].Pos = pos; Particles[0].Vel = Vector3f(0.0f, 0.0001f, 0.0f); Particles[0].LifetimeMillis = 0.0f; //生成2个transform feedback object和两个buffer //"OpenGL enforces a general limitation that the same resource cannot be bound for both input and output in the same draw call. //This means that if we want to update the particles in a vertex buffer we actually need two transform feedback buffers and toggle between them. //On frame 0 we will update the particles in buffer A and render the particles from buffer B and on frame 1 we will update the particles in buffer B and render the particles from buffer " //从上面可以看出我们之所以生成两个Transform Feedback Object和两个buffer是因为OpenGL要求我们不能在一次draw call里把同一个resource(这里指TFB和buffer)即作为输入也作为输出 //所以我们想要通过fist pass去记录一些数据信息,然后再将其渲染到屏幕上,我们必须通过切换两个TFO和buffer来实现 //记录到A的时候用B数据渲染,记录到B的时候通过A数据来渲染 glGenTransformFeedbacks(2, m_TransformFeedback);
m_IsFirst = false; } else { //第二次以后,顶点数量是未知的,因为GS是可以生成多个顶点数据的。 //"The system automatically tracks the number of vertices for us for each buffer and later uses that number internally when the buffer is used for input. " //从上面可知,transfor feedback buffer里的顶点数量系统会自己去track //我们只需通知用哪一个TFB绑定的buffer作为数据输入即可 glDrawTransformFeedback(GL_POINTS, m_TransformFeedback[m_CurrVB]); }
接下来让我们来看看Transform Feedback的更多高级使用: Multiple Output Steams Multiple streams of vertices can be declared as outputs in the geometry shader (通过stream我们可以把一些额外需要保存的信息保存到特定的stream里便于transform feedback buffer去访问并进行进一步的处理)
Using the stream layout qualifier – this layout qualifier may be applied globally, to an interface block, or to a single output declaration
Each stream is numbered, starting from zero, max number of streams – GL_MAX_VERTEX_STREAMS
When the stream number is given at global scope, all subsequently declared geometry shader outputs become members of that stream until another output stream layout qualifier is specified See how to declaration stream:
Multiple output stream’s built in GLSL functions: EmitStreamVertex(int stream) EndStreamVertex(int stream)
glTransformFeedbackVaryings() – tell OpenGL how those streams are mapped into transform feedback buffer (告诉OpenGL各个stream是怎么映射到transform feedback buffer的)
When multiple streams are active, it is required that variables associated with a single stream are not written into the same buffer binding point as those associated with any other stream(当多个stream声明激活的时候,我们必须将每一个stream写到不同的buffer binding point里)
gl_NextBuffer is used to signal that the following output variables are to be recorded into the buffer object bound to the next transform feedback binding point (gl_NexBuffer告诉OpenGL后面的数据将绑定到下一个transform feedback buffer)
if rasterization & fragment shader are enabled, the output variables belonging to stream 0 will be used to form primitives for rasterization and will be passed into the fragment shader. Output variables belonging to other streams will not be visible in the fragment shader and if transform feedback is not active, they will be discarded (这里需要注意,一旦rasterization 和 fragment shader被开启或者transform feedback没有被开启,那么geometry shader里面指定的out变量只有属于stream 0的才会被进行处理,其他都会被抛弃)
Note: When multiple output streams are used in a geometry shader, they must all have points as the primitive type (注意,当multiple output streams被开启时,geometry shader必须指定输出类型为point,当first pass的时候geometry shader指定输出类型为point,second pass的时候geometry shader可以针对第一次transform feedback记录的point数据进行处理输出triangle等)
Primitive Queries Reason: Geometry shader can emit a variable number of vertices per invocation (因为geometry shader会扩展出很多primitive和vertices,我们在访问一些跟transform feedback buffer相关的数据的时候就不那么直接 – 这里要提一下没有geometry shader,vertex shader结合transform feeback buffer的使用是一对一的输出,而geometry shader不一样,会有一堆多的primitive,vertices的输出)
Problem: The number of vertices recorded into transform feedback buffers when a geometry shader is present may not be easy to infer
Solution: Two types of queries are available to count both the number of primitives the geometry shader generates, and the number of primitives actually written into the transform feedback buffers(通过Primitive Queries我们可以得知geometry shader的primitives,vertices生成数量和实际被写入transform feedback buffer的primitive,vertices数量)
GL_PRIMITIVES_GENERATED – query counts the number of vertices output by the geometry shader – valid at any time & GL_TRANSFORM_FEEDBACK_PRIMITIVES_WRITTEN – query counts the number of vertices actually written into a transform feedback buffer – only valid when transform feedback is active
Due to geometry shader supports multiple transform feedback streams, primitive queries are indexed (因为geometry shader支持multiple transform feedback streams,所以primitive queries也是indexed的)
3D Picking
“The ability to match a mouse click on a window showing a 3D scene to the primitive (let’s assume a triangle) who was fortunate enough to be projected to the exact same pixel where the mouse hit is called 3D Picking.”
3D Picking实现的关键在于通过类似Shadow map的方式,把所有的primitive信息写入到一张picking texture里,当mouse点击的时候我们去查询所点击的primitive信息然后把该primitive渲染成我们想要的颜色即可。
实现步骤: First pass(picking pass) – 利用gDrawIndex, gObjectIndex, Primitive Index生成picking texture
通过类似生成Shaow map的方式,我们生成一个FRAMEBUFFER m_fbo,然后通过分别attach m_depthTexture和m_pickingTexture到GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0和GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT上,紧接着我们通过指定绘制到m_fbo的GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0(即我们attach的那个)上,这样一来当我们渲染到m_fbo的时候,attach到GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0的那个color texture就会得到渲染的picking texture,最后在我们我们在渲染之前需要指定m_fbo作为渲染到的FRAMEBUFFER。这样一来我们通过Picking Technique就能得到Picking texture。 这里也会生成depth texture,但我们并不会用到,指定生成depth texture的原因如下: “By combining a depth buffer in the process we guarantee that when several primitives are overlapping the same pixel we get the index of the top-most primitive (closest to the camera). “(注意我们需要结合depth buffer来保证我们生成的picking texture保存的primitive信息是离摄像机最近的)
for (uint i = 0 ; i < (int)ARRAY_SIZE_IN_ELEMENTS(gWorldPos) ; i++) { p.WorldPos(gWorldPos[i]); gPickingEffect.SetObjectIndex(i); gPickingEffect.SetWVP(p.GetWVPTrans()); gPSpider->Render(&gPickingEffect); }
gPickingTexture.DisableWriting(); }
最后gl_PrimitiveID是OpenGL build-in的变量,”This is a running index of the primitives which is automatically maintained by the system.”(代表我们绘制的primitive索引值,每一次draw都会从0开始。) 这里就引出了一个问题。我们如何得知我们渲染到picking texture里的primitive值0是指background还是被object遮挡的primitive了。 这也就是为什么我们在写入picking texture的时候,gl_PrimitiveID + 1的原因了。这样一来凡是primitive为0的都是background。
Render pass – 通过映射mouse click的pixel到picking texture,会得到鼠标点击到的gObjectIndex,gDrawIndex,gl_PrimitiveID信息,然后通过这些信息,我们把该点击的primitive通过simple color shader渲染成红色,然后再正常渲染两个spider即可。
// If the left mouse button is clicked check if it hit a triangle // and color it red if (m_leftMouseButton.IsPressed) { PickingTexture::PixelInfo Pixel = m_pickingTexture.ReadPixel(m_leftMouseButton.x, WINDOW_HEIGHT - m_leftMouseButton.y - 1); if (Pixel.PrimID != 0) { m_simpleColorEffect.Enable(); p.WorldPos(m_worldPos[(uint)Pixel.ObjectID]); m_simpleColorEffect.SetWVP(p.GetWVPTrans()); // Must compensate for the decrement in the FS! m_pMesh->Render((uint)Pixel.DrawID, (uint)Pixel.PrimID - 1); } }
// render the objects as usual m_lightingEffect.Enable(); m_lightingEffect.SetEyeWorldPos(m_pGameCamera->GetPos());
for (unsignedint i = 0 ; i < ARRAY_SIZE_IN_ELEMENTS(m_worldPos) ; i++) { p.WorldPos(m_worldPos[i]); m_lightingEffect.SetWVP(p.GetWVPTrans()); m_lightingEffect.SetWorldMatrix(p.GetWorldTrans()); m_pMesh->Render(NULL); } }
这里去读取picking texture里的信息的时候,要注意的一点是,鼠标获取得到的坐标信息和我们去查询texture的坐标系是不一致的,这里需要转换。 一下来源于Glut Mouse Coordinates “In “window” coordinate, the origin (0,0) is top left of the viewport.In OpenGL the origin is bottom left of the viewport. When you click glut give you the window coordinate. All you have to do is calculate this: y = height_of_viewport - y - 1.
Edit: Notice that you compare a screen coordinate (mouse click) with an object coordinate (your rectangle). This is fine if you use a perspective projection like this glOrtho(0,0,viewport_width,viewport_height). If not you need to call gluProject to map each corner of your rectangle in screen coordinate. “ 从上面可以看出,glut获取的mouse坐标系是以左上角为(0,0)点。而OpenGL viewport的(0,0)点时左下角,所以我们需要通过下列方式去转换映射点:
在得到正确的映射值后,我们将查询到的gObjectIndex,gDrawIndex,gl_PrimitiveID当做信息传入void Mesh::Render(unsigned int DrawIndex, unsigned int PrimID)去指定渲染特定mesh的特定primitive成红色。这里要注意的一点是因为mesh里的primitive索引是从0开始的,但我们之前存储的primitive index是+1的,所以这里我们需要恢复原有正确的值去指定渲染正确的primitive。
1 2
// Must compensate for the decrement in the FS! m_pMesh->Render((uint)Pixel.DrawID, (uint)Pixel.PrimID - 1);
The tessellation process doesn’t operate on OpenGL’s classic geometric primitives: points, lines, and triangles, but uses a new primitive called a patch (Tessellation shader就是针对patch来进行处理的而并非点,线,三角形)
Patch is just an ordered list of vertices (在tessellation shader里面比较重要的概念就是这个patch,patch是一系列的顶点,OpenGL规定patch的vertex数量必须至少大于等于3)。这里的Patch我们可以理解为一个包含了几何图形的所有Control Points(CP)的集合。Control Points会决定这个几何图形最终的形态。
Tessellation Control Shader(TCS) “The control shader calculates a set of numbers called Tessellation Levels (TL). The TLs determine the Tessellation level of detail - how many triangles to generate for the patch.” 可以看出TCS并不是负责顶点的细分而是负责指定细分的规则(如何细分,细分程度)。
Note: “It is executed once per CP in the output patch”
Primitive Generator (Fixed function) “OpenGL passes the output of the tessellation control shader to the primitive generator, which generates the mesh of geometric primitives and tessellation coordinates that the tessellation evaluation shader stage uses.”(PG之后会输出domain细分后的顶点和顶点纹理坐标信息,通过顶点纹理信息TES会算出对应的顶点位置信息)
Tessellation Evaluation Shader(TES) The TES is executed on all generated domain locations.Positions each of the vertices in the final mesh (TES是针对从tessellation control shader和Primitive Generator通过细分后所有patch相关的顶点来进行运算,通过各顶点的gl_TessCoord(顶点在patch里的相对坐标信息)按不同Domain的纹理坐标计算方式计算出相应的纹理坐标,位置信息和法线信息,从而实现细分多边形和修改顶点信息效果)
// attributes of the input CPs in vec3 WorldPos_CS_in[]; in vec2 TexCoord_CS_in[]; in vec3 Normal_CS_in[]; // attributes of the output CPs out vec3 WorldPos_ES_in[]; out vec2 TexCoord_ES_in[]; out vec3 Normal_ES_in[]; // 根据patch各顶点到camera的距离决定patch的细分程度 floatGetTessLevel(float Distance0, float Distance1) { float AvgDistance = (Distance0 + Distance1) / 2.0; if (AvgDistance <= 2.0) { return10.0; } elseif (AvgDistance <= 5.0) { return7.0; } else { return3.0; } } voidmain() { // Set the control points of the output patch // 记录下patch的control point的原始顶点信息,在TES中会参与就算,算出细分的顶点的位置信息 // **gl_InvocationID** is used to access the specific vertex of a patch (gl_InvocationID 用于访问传入patch里的特定顶点) // 之前我们指定patch的顶点数量是3,TCS是针对patch的顶点来执行的,所以每一个patch会执行3次TCS TexCoord_ES_in[gl_InvocationID] = TexCoord_CS_in[gl_InvocationID]; Normal_ES_in[gl_InvocationID] = Normal_CS_in[gl_InvocationID]; WorldPos_ES_in[gl_InvocationID] = WorldPos_CS_in[gl_InvocationID]; // Calculate the distance from the camera to the three control points // 算出patch各顶点到camera的距离 float EyeToVertexDistance0 = distance(gEyeWorldPos, WorldPos_ES_in[0]); float EyeToVertexDistance1 = distance(gEyeWorldPos, WorldPos_ES_in[1]); float EyeToVertexDistance2 = distance(gEyeWorldPos, WorldPos_ES_in[2]); // Calculate the tessellation levels // 根据patch各顶点到camera的距离设置细分方式和细分程度 // **gl_TessLevelInner** // Specify how the interior of the domain is subdivided and stored in a two element array named gl_TessLevelInner(指定多边形内部如何细分) // **gl_TessLevelOuter** // Control how the perimeter of the domain is subdivided, and is stored in an implicitly declared four-element array named gl_TessLevelOuter(指定多边形边界上的边被如何细分) // gl_TessLevelInner & gl_TessLevelOuter 根据Domain的类型不同会有不同的含义,参见前面提到的Domain // 我们也可以在程序里通过调用glPatchParameterfv()指定inner和outer的数值 gl_TessLevelOuter[0] = GetTessLevel(EyeToVertexDistance1, EyeToVertexDistance2); gl_TessLevelOuter[1] = GetTessLevel(EyeToVertexDistance2, EyeToVertexDistance0); gl_TessLevelOuter[2] = GetTessLevel(EyeToVertexDistance0, EyeToVertexDistance1); gl_TessLevelInner[0] = gl_TessLevelOuter[2]; }
“The Vertex Array Object (a.k.a VAO) is a special type of object that encapsulates all the data that is associated with the vertex processor. Instead of containing the actual data, it holds references to the vertex buffers, the index buffer and the layout specification of the vertex itself.”
“VAOs store all of the links between the attributes and your VBOs with raw vertex data.”
unsignedint NumVertices = 0; unsignedint NumIndices = 0; // Count the number of vertices and indices for (unsignedint i = 0 ; i < m_Entries.size() ; i++) { m_Entries[i].MaterialIndex = pScene->mMeshes[i]->mMaterialIndex; m_Entries[i].NumIndices = pScene->mMeshes[i]->mNumFaces * 3; m_Entries[i].BaseVertex = NumVertices; m_Entries[i].BaseIndex = NumIndices; NumVertices += pScene->mMeshes[i]->mNumVertices; NumIndices += m_Entries[i].NumIndices; } // Reserve space in the vectors for the vertex attributes and indices Positions.reserve(NumVertices); Normals.reserve(NumVertices); TexCoords.reserve(NumVertices); Indices.reserve(NumIndices);
// Initialize the meshes in the scene one by one for (unsignedint i = 0 ; i < m_Entries.size() ; i++) { const aiMesh* paiMesh = pScene->mMeshes[i]; InitMesh(paiMesh, Positions, Normals, TexCoords, Indices); }
if (!InitMaterials(pScene, Filename)) { returnfalse; }
// Generate and populate the buffers with vertex attributes and the indices // 下面就是存储成SOA的格式 glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, m_Buffers[POS_VB]); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(Positions[0]) * Positions.size(), &Positions[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); glEnableVertexAttribArray(POSITION_LOCATION); glVertexAttribPointer(POSITION_LOCATION, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, 0);
// Populate the index buffer for (unsignedint i = 0 ; i < paiMesh->mNumFaces ; i++) { const aiFace& Face = paiMesh->mFaces[i]; assert(Face.mNumIndices == 3); Indices.push_back(Face.mIndices[0]); Indices.push_back(Face.mIndices[1]); Indices.push_back(Face.mIndices[2]); } }
“Instanced rendering means that we can render multiple instances in a single draw call and provide each instance with some unique attributes.”(在一次draw call里绘制多个同一个instance)
Using the Instance Counter in Shaders: The index of the current instance is available to the vertex shader in the built-in variable gl_InstanceID. This variable is implicitly declared as an integer. It starts counting from zero and counts up one each time an instance is rendered.
Instancing Redux: Steps:
Create some vertex shader inputs that you intend to be instanced
Set the vertex attribute divisors with glVertexAttribDivisor()
Use the gl_InstanceID built-in variable in the vertex shader
Use the instanced versions of the rendering functions such as glDrawArraysInstanced() ……
for (unsignedint i = 0; i < 4 ; i++) { glEnableVertexAttribArray(WVP_LOCATION + i); // Note: "A vertex attribute can contain no more than 4 floating points or integers." // 因为vertex attribute不能超过4个float或integers,所以我们需要针对mat4每一行进行指定访问方式 glVertexAttribPointer(WVP_LOCATION + i, 4, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Matrix4f), (const GLvoid*)(sizeof(GLfloat) * i * 4)); // 这里是"makes this an instance data rather than vertex data." // 第一个参数指明特定attribute是instance data而非vertex data, // 第二个参数指明instance data的使用频率,比如1表示每一个instance渲染后就访问下一个atrribute值,2表示每两个 glVertexAttribDivisor(WVP_LOCATION + i, 1); }
lighting.vs #version 330 layout (location = 0) in vec3 Position; layout (location = 1) in vec2 TexCoord; layout (location = 2) in vec3 Normal; // 这里注意因为vertex attribute不能超过4个float或integers,我们前面指定了每一个mat4四次vertex attribute // 所以这里WVP location = 3 而 World location = 7 layout (location = 3) in mat4 WVP; layout (location = 7) in mat4 World; out vec2 TexCoord0; out vec3 Normal0; out vec3 WorldPos0; // "Since integers cannot be interpolated by the rasterizer we have to mark the output variable as 'flat' (forgetting to do that will trigger a compiler error)." // 因为integers不能被rasterizer interpolated,所以我们需要使用'flat'关键词避免编译错误 flat out int InstanceID; voidmain() { gl_Position = WVP * vec4(Position, 1.0); TexCoord0 = TexCoord; Normal0 = (World * vec4(Normal, 0.0)).xyz; WorldPos0 = (World * vec4(Position, 1.0)).xyz; InstanceID = gl_InstanceID; }
Final Effect:
Note: gl_InstanceID is always present in the vertex shader, even when the current drawing command is not one of the instanced ones.
GLFX - An OpenGL Effect Library
首先让我们了解一下,什么是Effect file? “An effect is a text file that can potentially contain multiple shaders and functions and makes it easy to combine them together into programs. This overcomes the limitation of the glShaderSource() function that requires you to specify the text of a single shader stage.” 可以看出,通过effect file,我们可以把所有shader写到一个文件里,不用再创建针对各个stage的shader的文件。这样一来我们在shader里定义的结构体就能在多个shader共用。
那什么是GLFX了? “Effects system for OpenGL and OpenGL ES” GLFX提供了方便的接口去转换effect file到GLSL program.
因为所有shader内容都写在一个文件里了,所以支持共用struct定义,不用再定义一个个in or out variables
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
structVSoutput { vec2 TexCoord; vec3 Normal; };
shader VSmain(in vec3 Pos, in vec2 TexCoord, in vec3 Normal, out VSOutput VSout) { // do some transformations and update 'VSout' VSout.TexCoord = TexCoord; VSout.Normal = Normal; }
shader FSmain(in VSOutput FSin, out vec4 FragColor) { // 'FSin' matches 'VSout' from the VS. Use it // to do lighting calculations and write the final output to 'FragColor' }
be passed between shader stages. If you need to pass it as a whole to another function you will need to copy the contents to a struct. For example: interface foo { flat int a; noperspective float b; };
// specify the color buffer to be drawn into, we will output buffer data for each color buffer in FS with out key word variable // 这里应对的是FS里指定的out输出 glDrawBuffers(ARRAY_SIZE_IN_ELEMENTS(drawbuffers), drawbuffers);
......
returntrue; }
geometry_pass.vs // VS没什么变化,只是把我们需要保存的Position,TexCoord,Normal分别转换透视投影坐标系和世界坐标系里 #version 330 layout (location = 0) in vec3 Position; layout (location = 1) in vec2 TexCoord; layout (location = 2) in vec3 Normal;
uniform mat4 gWVP; uniform mat4 gWorld; out vec2 TexCoord0; out vec3 Normal0; out vec3 WorldPos0;
geometry_pass.fs // FS负责把转换后的Position,Diffuse,Normal,TexCoordOut输出到我们之前绑定的GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT*上 #version 330 in vec2 TexCoord0; in vec3 Normal0; in vec3 WorldPos0;
staticvoidDSLightPass() { // Bound frame buffer target 0 to draw state, we will copy four color buffer to this buffer later // 因为glBlitFramebuffer()函数是把GL_READ_FRAMEBUFFER的target copy到GL_DRAW_FRAMEBUFFER的target上, // 所以我们要声明Frame buffer 0作为我们最终的目的地 glBindFramebuffer(GL_DRAW_FRAMEBUFFER, 0);
// Bound frame buffer m_FBO to reading state, // we will copy four color buffer that attach to m_FBO to frame buffer target 0 later // BindForReading()就是设置m_FBO作为glBlitFramebuffer()里的copy来源, // 所以需要设置成GL_READ_FRAMEBUFFER gGbuffer.BindForReading();
// Color buffer for position // Set color buffer source for copying // 因为一次只能从一个texture里copy,所以我们需要指定是copy哪一个 gGbuffer.SetReadBuffer(GBuffer::GBUFFER_TEXTURE_TYPE_POSITION); // Set buffer copy info glBlitFramebuffer(0, 0, WINDOW_WIDTH, WINDOW_HEIGHT, 0, 0, halfwidth, halfheight, GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT, GL_LINEAR);
// Color buffer for diffuses gGbuffer.SetReadBuffer(GBuffer::GBUFFER_TEXTURE_TYPE_DIFFUSE); glBlitFramebuffer(0, 0, WINDOW_WIDTH, WINDOW_HEIGHT, 0,halfheight, halfwidth, WINDOW_HEIGHT, GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT, GL_LINEAR);
// Color buffer for normal gGbuffer.SetReadBuffer(GBuffer::GBUFFER_TEXTURE_TYPE_NORMAL); glBlitFramebuffer(0, 0, WINDOW_WIDTH, WINDOW_HEIGHT, halfwidth,halfheight, WINDOW_WIDTH, WINDOW_HEIGHT, GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT, GL_LINEAR);
// Color buffer for TexCoor gGbuffer.SetReadBuffer(GBuffer::GBUFFER_TEXTURE_TYPE_TEXCOORD); glBlitFramebuffer(0, 0, WINDOW_WIDTH, WINDOW_HEIGHT, halfwidth,0, WINDOW_WIDTH, halfheight, GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT, GL_LINEAR); }
Point Light因为是范围光,所以我们需要知道Point Light所影响的范围去触发对应Pixel的光照计算。这里涉及到一个Point Light的Point Light光照削弱方程。这里我也没详细看了,想了解的可以去看一下。通过方程我们得出了Point Light的有效范围,这样一来我们只需要以Point Light所在位置为圆心绘制一个Sphere就能触发正确的Point Light光照计算了。 Point Light:
Render the objects as usual into the G buffer so that the depth buffer will be properly populated.
Disable writing into the depth buffer. From now on we want it to be read-only
Disable back face culling. We want the rasterizer to process all polygons of the sphere.
Set the stencil test to always succeed. What we really care about is the stencil operation.
Configure the stencil operation for the back facing polygons to increment the value in the stencil buffer when the depth test fails but to keep it unchanged when either depth test or stencil test succeed.
Configure the stencil operation for the front facing polygons to decrement the value in the stencil buffer when the depth test fails but to keep it unchanged when either depth test or stencil test succeed.
Render the light sphere.(only when the stencil value of the pixel is different from zero)
// We need the stencil test to be enabled but we want it // to succeed always. Only the depth test matters. // 指定stencil text always success, // 因为这里我只需要通过设定stencil buffer修改规则就能得到我们要的值了 glStencilFunc(GL_ALWAYS, 0, 0);
// We need stencil to be enabled in the stencil pass to get the stencil buffer // updated and we also need it in the light pass because we render the light // only if the stencil passes. glEnable(GL_STENCIL_TEST);
for (unsignedint i = 0 ; i < ARRAY_SIZE_IN_ELEMENTS(m_pointLight); i++) { DSStencilPass(i); DSPointLightPass(i); }
// The directional light does not need a stencil test because its volume // is unlimited and the final pass simply copies the texture. glDisable(GL_STENCIL_TEST);
“assimp is a library to load and process geometric scenes from various data formats. It is tailored at typical game scenarios by supporting a node hierarchy, static or skinned meshes, materials, bone animations and potential texture data. The library is not designed for speed, it is primarily useful for importing assets from various sources once and storing it in a engine-specific format for easy and fast every-day-loading. “
“open3mod is a Windows-based model viewer. It loads all file formats that Assimp supports and is perfectly suited to quickly inspect 3d assets.”
主要用于快速查看各种资源格式的模型。
GIMP
GNU Image Manipulation Program (GIMP) is a cross-platform image editor available for GNU/Linux, OS X, Windows and more operating systems. GIMPDownloadLink
.Net Framework还包含.NET公共语言运行库(Common Language Runtime, CLR),它负责管理用.NET库开发的所有应用程序的执行
Using .NET Framework
Tools
Visual Studio
VCE(for C#)
相关概念
FCL(Framework Class Library)
“The FCL is a set of DLL assemblies that contain several thousand type definitions in which each type exposes some functionality.”(提供了大量功能的现有DLL库)
Metadata
“There are two main types of tables: tables that describe the types and members defined in your source code and tables that describe the types and members referenced by your source code.”(包含了源代码里类型的定义,对象的索引等信息)
IL(Intermediate Language)
“IL is a CPU-independent machine language created by Microsoft after consultation with several external commercial and academic language/compiler writers.”(CPU无关的中间语言,用来抽象编译后的高阶语言,在JIT中会被编译成特定OS和目标机器架构的机器代码)
“The common language runtime (CLR) is just what its name says it is: a runtime that is usable by different and varied programming languages. The core features of the CLR (such as memory management, assembly loading, security, exception handling, and thread synchronization) are available to any and all programming languages that target it” – 《CLR Via C# Fourth Edition - Jeffrey Richter》(公共语言运行库提供了内存管理,异常处理,线程同步等功能)
CTS(Common Type System)
“Describes how types are defined and how they behave. Defines the rules governing type inheritance, virtual methods, object lifetime, and so on.”
CLS(Common Language Specification)
“Details for compiler vendors the minimum set of features their compilers must support if these compilers are to generate types compatible with other components written by other CLS-compliant languages on top of the CLR.”(通用语言规范定义了通用语言之间类型交互的基本规范)
JIT(Just-In-Time) 把CIL编译为专用于OS和目标机器结构的机器代码 e.g. 从上面可以看出,之前生成的IL会被JIT在运行时编译成对应的本地机器代码。当同样的方法再次调用时,就不需要JIT进行IL到本地机器代码的编译,直接调用之前编译好的机器代码即可。
这里有个Unsafe code的概念值得注意。 Unsafe code is allowed to work directly with memory addresses and can manipulate bytes at these addresses. /unsafe compiler switch to control whether allow to executing unsafe code(只有编译器开启了/unsafe标志才允许执行unsafe code(e.g. 直接操作内存地址进行修改)) PEVerify.exe可用不查看Assembly里是否有unsafe code。
程序集
编译程序时所创建的CIL代码存储在一个程序集中(e.g. .exe .dll) 程序集包含程序用到的相关数据信息(Assemblies contains all module’s Metadata and IL)
Note: PDB(program Database) file helps the debugger find local variables and map the IL instructions to the source code. NGen.exe tool can compiles all of an assembly’s IL code into native code and saves the resulting native code to a file on disk.(avoid compilation at run time)
Note: “C++ is unique in that it is the only compiler that allows the developer to write both managed and unmanaged code and have it emitted into a single module.”
Only record some difference between C# and C++/Java
delegate
delegates – type-safe Unmanaged C/C++ callback functions are not type-safe 首先要知道的是delegate在C#里类型安全的(即有有编译时的类型检查) C++里是不是类型安全的
在调用delegate的时候,CLR提供了当reference type绑定方法到delegate的时covariance和contra-variance的支持。 Covariance means that a method can return a type that is derived from the delegate’s return type.(reference type的方法的返回类型可以是delegate指定返回类型的子类) Contra-variance means that a method can take a parameter that is a base of the delegate’s parameter type.(reference type的方法的参数可以是delegate指定参数类型的父类) The reason why value types and void cannot be used for covariance and contra-variance is because the memory structure for these things varies, whereas the memory structure for reference type is always a pointer.(value type和void不支持上述功能)
Class qualifier internal class – only code in current project can access (default) public class – other project code can access
abstract class – abstract class sealed class – cant not be inheritated
Note: Compiler is not allowed derived class’s access privileges higher than parent class
e.g.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
internalclassMyBase { publicMyBase() { } } //Cant do like this due to Child class access previlage is higher than parent class publicclassMyChild/*: MyBase*/ { publicMyChild() {
} }
support extends multiple interface Note: base class must be write down first when we inherites from one class and extends several interface abstract & sealed can not be used by interface due to no implementation in interface (abstract & sealed qualifier are meaningless)
Static constructor & Static class 静态构造函数只会被调用一次且属于整个类 静态类不能拥有实例构造函数且只能有static成员
privateint IntA { get { return m_A; } //Can not be public due to IntA's access privilege is lower than public //public set set { m_A = value; } } privateint m_A; }
member function override key word can hide base function(works with polymorphism) Access base function that has been hiden uses base key word in child class
Interface member all interface member must be public can not use static, virtual, abstract, sealed
Interface implementation explicit implementation – only can be accessed through interface (return type interface.functionanme(para)) implicit implementation – can be accessd through both interface and class
partial class definition & partial property can put class member, property, method, field into several files(partial key word) Partial property is always static and withought return value
Struct & Class
Struct is value type 在栈上分配内存 栈回收快速 传递的是值 转换为reference type会触发boxing引发堆上的额外内存分配 Class is reference type 在堆上分配内存 GC管理 传递的是索引 那么什么时候定义struct,什么时候定义class了? 一下来至MSDNChoosing Between Class and Struct ✓ CONSIDER defining a struct instead of a class if instances of the type are small and commonly short-lived or are commonly embedded in other objects. 如果生命周期短,并被包含在其他类里而已考虑使用struct
X AVOID defining a struct unless the type has all of the following characteristics: It logically represents a single value, similar to primitive types (int, double, etc.). It has an instance size under 16 bytes. It is immutable. It will not have to be boxed frequently. In all other cases, you should define your types as classes. 可以看出只有在数据简单,不可变,不需要频繁boxing的时候才会选择定义struct。
Shallow copy & Deep copy Shallow copy will only copy value type member, reference type member will use original one(System.Object.MemberwiseClone())
Deep copy will copy all member value instead of reference(implememnt ICloneable::Clone())
Collection class (System.Collection)
好比C++里的STL里的container Our own collection (extends CollectionBase Class || DictionaryBase)
//If any child is bigger than parent, //then we swap it and do adjust for child again to make sure meet max heap definition if (max_index != parentindex) { Swap(max_index, parentindex); HeapifyFromBeginningToEnd(max_index, length); } }
//O(log(N)) privatevoidHeapifyFromEndToBeginning(int index) { if (index >= mCount) { return; } while (index > 0) { int parentindex = (index - 1) / 2; if (mComparer.Compare(mList[parentindex].Value, mList[index].Value) > 0) { Swap(parentindex, index); index = parentindex; } else { break; } } }
//通过初试数据构建最大堆 ////O(N*Log(N)) privatevoidBuildingHeap() { if (mList != null) { for (int i = mList.Count / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //1.2 Adjust heap //Make sure meet max heap definition //Max Heap definition: // (k(i) >= k(2i) && k(i) >= k(2i+1)) (1 <= i <= n/2) HeapifyFromBeginningToEnd(i, mList.Count); } } }
//1. Build max heap // 1.1 Init heap //Assume we construct max heap BuildingHeap(); //2. Sort heap //这里花O(n),跟数据数量有关 for (int i = mList.Count - 1; i > 0; i--) { //swap first element and last element //do adjust heap process again to make sure the new array are still max heap Swap(i, 0); //Due to we already building max heap before, //so we just need to adjust for index 0 after we swap first and last element HeapifyFromBeginningToEnd(0, i); } } else { Console.Write("mList == null"); } }
Extension Methods “It allows you to define a static method that you can invoke using instance method syntax.”(Extension Methods最主要的好处就在于当你无法给特定类或结构定义方法的时候,你可以通过定义extension method来为该类或结构添加方法,使用的时候就跟在类里定义方法一样,通过实例就能调用。) 定义Extension Method首先必须定义在一个静态类里,且方法为静态方法,并且第一个参数类型前要加this关键词,this后面跟的就是我们要extension的类。
publicstaticclassStringBuilderExtensions { publicstatic Int32 Indexof(this StringBuilder sb, Char value) { for (Int32 index = 0; index < sb.Length; index++) { if (sb[index] == value) { return index; } } return-1; } }
staticvoidMain(string[] args) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Hello. My name is Tony."); Int32 index = sb.Indexof('T'); Console.WriteLine("sb.Indexof('T') = " + index); }
Type comparasion System.Object.GetType() && typeof() && is operator – is specific type or type can be cast
boxing – cast value type into System.Object type(shollow copy) or interface type that is implemented by value type
unboxing – boxing reverse process
Value comparasion operator overloading – must be static IComparable – compare object’s data with the same type && IComparer – compare two object with different type or the same type
Conversion
Conversion operator implici explicit e.g.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
classA { publicstaticimplicitoperatorB(A a) { ...... } }
classB { publicstaticexplicitoperatorA(B b) { ...... } }
as operator as Suit case
operand type is type
operand type can be casted into type implicitly
operand can be boxing into type
Generics
C++里是template实现 System.Collections.Generic value type can not be initilized with null Problem
null (value type or reference type)
default key word – if it is reference type, initilized with null. otherwise use default value
type
constraining where key words e.g. class A: where T:B 9( T must inherite from B)
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Collections;
namespaceCSharpStudy { classProgram { //Can not instantiation with int when where T1 : class //public class GenericClass<T1> where T1 : class publicclassGenericClass<T1> : IEnumerable<T1> whereT1 : struct { private List<T1> m_Member = new List<T1>();
以下英文内容来至《CLR via C#》 Hosting allows any application to use the features of the common language runtime(CLR). Furthermore, hosting allows applications the ability to offer customization and extensibility via programming. Extensibility means that third-party code will be running inside your process.
The hosting application can call methods defined by ICLRMetaHost interface to:
Set Host managers. Tell the CLR that the host wants to be involved in making decisions related to memory allocations, thread scheduling/synchronization, assembly loading, and more. The host can also state that it wants notifications of garbage collection starts and stops and when certain operations time out.
Get CLR managers. Tell the CLR to prevent the use of some classes/members. In addition, the host can tell which code can and can’t be debugged and which methods in the host should be called when a special event—such as an AppDomain unload, CLR stop, or stack overflow exception—occurs.
Initialize and start the CLR.
Load an assembly and execute code in it.
Stop the CLR, thus preventing any more managed code from running in the Windows process.
Hosting(allows any application to offer CLR features) Benifits:
Programming can be done in any programming language.
Code is just-in-time (JIT)–compiled for speed (versus being interpreted).
Code uses garbage collection to avoid memory leaks and corruption.
Code runs in a secure sandbox.
The host doesn’t need to worry about providing a rich development environment. The host makes use of existing technologies: languages, compilers, editors, debuggers, profilers, and more. 从上面所有内容可以看出Hosting可以让我们去利用CLR的特性,我们而已通过Host去设定很多CLR相关的设定(比如GC,Memory Manager……),初始化CLR,创建出默认的AppDomain,通过CLR去加载Assemly到AppDomain然后执行。
AppDomain
AppDomain allows third-party untrusted code to run in an existing proceess, and the CLR guarantees that the data structures, code, and security context will not be exploited or compromised.(AppDomain允许不可信的代码在当前进程执行,CLR会去确保数据结构,代码等安全问题) AppDomain和CLR的关系: “AppDomains are a CLR feature.”
“When the CLR COM server initializes, it creates an AppDomain. An AppDomain is a logical container for a set of assemblies. The first AppDomain created when the CLR is initialized is called the default AppDomain; this AppDomain is destroyed only when the Windows process terminates.”(AppDomain是一个assemblies集合的容器,当CLR初始化的时候会创建默认的AppDOmain,这个AppDomain只能在程序结束的时候被终止)
The whole purpose of an AppDomain is to provide isolation. Here are the specific features offered by an AppDomain(AppDomain的主要目的是为了实现程序隔离):
Objects created by code in one AppDomain cannot be accessed directly by code in another AppDomain When(确保不同AppDomain里的Object不会被其他AppDomain访问)
AppDomains can be unloaded(AppDomain可以被unload)
AppDomains can be individually secured(通过设定AppDomain的permission用于确保assembly的一些权限)
AppDomains can be individually configured(设置AppDomian的配置,影响如何去加载Assemlies等)
这里提到AppDomain的程序隔离功能,那就不得不说一下Process了。 “Process isolation prevents security holes, data corruption, and other unpredictable behaviors from occurring, making Windows and the applications running on it robust.” 这里Process可以理解为进程面上的程序隔离,而AppDomain可以理解为进程内的程序隔离(一个进程可以创建多个AppDomain) 让我们看一下程序是如何在Process,AppDomain还有CLR下工作的: 可以看出一个Process下创建了多个AppDomain,每一个AppDomain加载了特定的Assembly,每一个AppDomain有自己的LoaderHeap,每一个LoaderHeap记录了该AppDomain所访问过的type,当调用type的method的时候,IL code会被JIT运行时编译到对应的机器代码执行。 普通的AppDomain之间的Assembly是完全隔离的,所以就算多个AppDomain引用了同一个Assembly,他们也不会共享数据和内存。 但上图有一个比较特殊的AppDomain,叫做Domain-Neutrl Assemblies。 这个Domain的主要目的是共享一些通用的Assemblys,加载在这个AppDomian下的Assemblys可以被所有的AppDomains访问。 虽然Assembly在AppDomain之间是完全隔离的,但不同AppDomain创建的objects还是可以相互访问的。 让我们看看不同AppDomain创建的objeccts如何相互访问的:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Collections; using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices; using System.Threading; using System.Runtime; using System.Runtime.Remoting;
namespaceCSharpDeepStudy { classProgram { #region Hosting and AppDomain Study // Instances can be marshaled-by-reference across AppDomain boundaries [Serializable] publicsealedclassMarshalByRefType : MarshalByRefObject { publicMarshalByRefType() { Console.WriteLine("{0} ctor running in {1}", this.GetType().ToString(), Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName); }
publicvoidSomeMethod() { Console.WriteLine("Executing in " + Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName); }
public MarshalByValType MethodWithReturn() { Console.WriteLine("Executing in " + Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName); MarshalByValType t = new MarshalByValType(); return t; }
public NonMarshalableType MethodArgAndReturn(String callingdomainname) { Console.WriteLine("Calling from {0} to {1}", callingdomainname, Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName); NonMarshalableType t = new NonMarshalableType(); return t; } }
// Instances can be marshaled-by-value across AppDomain boundaries [Serializable] publicsealedclassMarshalByValType : Object { private DateTime m_CreationTime = DateTime.Now;
publicMarshalByValType() { Console.WriteLine("{0} ctor running in {1}, Created on {2:D}", this.GetType().ToString(), Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName, m_CreationTime); }
//Get the assembly that contains the main method Assembly mainassembly = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly(); String exeassembly = mainassembly.FullName; Console.WriteLine("Assembly's that contains main method name is " + exeassembly);
//Accessing Objects Across AppDomain Boundaries //Cross-AppDomain Communication using marshal-by-reference AppDomain ad2 = null; ad2 = AppDomain.CreateDomain("AD2", null, null); MarshalByRefType mbrt = null; mbrt = (MarshalByRefType)ad2.CreateInstanceAndUnwrap(exeassembly, typeof(MarshalByRefType).FullName); Console.WriteLine("Type = {0}", mbrt.GetType()); //Prove that we got a reference to a proxy object Console.WriteLine("Is proxy = {0}", RemotingServices.IsTransparentProxy(mbrt)); //Call method in the AppDomain owning the objects mbrt.SomeMethod(); //Unload the new AppDomian AppDomain.Unload(ad2); //try access mbrt after we unload AppDomain it owned try { mbrt.SomeMethod(); Console.WriteLine("Successful call SomeMehtod()"); } catch (AppDomainUnloadedException) { Console.WriteLine("Failed call SomeMethod()"); }
//Cross-AppDomain Communication using Marshal-by-value //Create new AppDomain ad2 = AppDomain.CreateDomain("AD3", null, null); mbrt = (MarshalByRefType)ad2.CreateInstanceAndUnwrap(exeassembly, typeof(MarshalByRefType).FullName);
MarshalByValType mbvt = mbrt.MethodWithReturn(); //Prove that we did NOT get a reference to a proxy object Console.WriteLine("Is Proxy={0}", RemotingServices.IsTransparentProxy(mbvt)); //Try call method on real object Console.WriteLine("Returned object created " + mbvt.ToString()); //Unload AppDomain again AppDomain.Unload(ad2); //try access method on real object again try { Console.WriteLine("Returned object created " + mbvt.ToString()); Console.WriteLine("Successful call."); } catch (AppDomainUnloadedException) { Console.WriteLine("Failed call."); }
//Cross-AppDomain Communication Using non-marshalable type ad2 = AppDomain.CreateDomain("AD4", null, null); //Load assembly into the new AppDoamin mbrt = (MarshalByRefType)ad2.CreateInstanceAndUnwrap(exeassembly, typeof(MarshalByRefType).FullName);
//call the object method to get non-marshalable object try { NonMarshalableType nmt = mbrt.MethodArgAndReturn(callingdomainname); } catch (System.Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e.ToString()); } }
staticvoidMain(string[] args) { #region Hosting and AppDomain Study Marshalling(); #endregion
Console.ReadKey(); } } }
上面的测试主要是针对下面三种情况:
Cross-AppDomain Communication Using Marshal-by-Reference 从上面可以看出当我们Marshal-by-Reference between AppDomain的时候,我们需要继承至MarshalByRefObject。(通过RemotingServices.IsTransparentProxy检查是否是Proxy) 底层是通过在Destination AppDomain生成的Proxy Type信息,其中还生成了instane fields去记录了哪一个AppDomain真正拥有这个type,如何在该AppDomain下找到这个real object去实现Reference的。 这样就说得通当我们关掉创建Prox Type的AppDomain后,再次通过Prox Type调用就无法通过了,因为通过调用AppDomain.Unload(),所有在该AppDomain里的assemblies和通过assemblies里的信息创建的对象都被释放回收了。 Note: “although you can access fields of a type derived from MarshalByRefObject, the performance is particularly bad because the CLR really ends up calling methods to perform the field access.”
Cross-AppDomain Communication Using Marshal-by-Value 当我们Marshal-by-Value时不需要继承至MarshalByRefObject,但需要确保MarshalByValType是[Serializable]的。 因为底层实现是通过序列化和反序列化实现Destination AppDomain加载并生成对应type信息。
Cross-AppDomain Communication Using Non-Marshalable Types 最后一个是因为我们采用Marshal-by-Value但却没有把NonMarshalableType设置成[Serializable]导致在Serialize NonMarshalableType到Destination AppDomain的时候抛异常。 针对AppDomain问题我没有深入学习,如有不对之处欢迎指出,详情请参考《CLR via C#》 Hosting,CLR,AppDomain,Process,Assemly关系作用总结: Hosting使我们可以去利用CLR的特性,通过Host可以设定很多CLR相关的设定(比如GC,Memory Manager……)。 当CLR初始化完成后,会创建出默认的AppDomain。 通过CLR去加载Assemly到AppDomain然后执行。 一个Process可以有多个AppDomian。 每个AppDomain有自己的Loader Heap去记录加载到AppDomain里的Type信息。 当调用Type的method的时候,IL code会被JIT运行时编译到对应的机器代码执行。 普通的AppDomain之间的Assembly是完全隔离的,所以就算多个AppDomain引用了同一个Assembly,他们也不会共享数据和内存。 但加载在这个Domain-Neutrl Assemblies AppDomian下的Assemblys可以被所有的AppDomains访问。 虽然Assembly在AppDomain之间是完全隔离的,但不同AppDomain创建的objects还是可以通过Marshal-by-Value和Marshal-by-Reference方式相互访问的。 关于AppDomain的更多内容参考《CLR via C#》 – CLR Hosting and AppDomains章节(e.g. AppDomain Monitoring, How Hosts Use AppDomians……) Note: 在Windows上默认的AppDomain的名字是是***.exe(执行的程序)
这样一来我们就实现了动态加载Assemble,然后通过反射调用里面特定类的特定方法。 关于反射使用Event并动态创建Delegate参考《CLR vir C#》 – Assembly Loading and Reflection章节
注意下面讲到的内容和书上的测试结果不一致,暂时不知道为什么。结论对错暂时不予置评。 如果我们要频繁的通过反射去访问特定类里的方法和成员,我们会采用存储Type,MemberInfo-derived Object到collection的方式,然后再通过collection去访问。 “Type and MemberInfo-derived objects require a lot of memory.” 但Type,MemberInfo及子类存储了大量的类型信息,会耗费大量的内存。 如何解决这个问题了? “Developers who are saving/caching a lot of Type and MemberInfoderived objects can reduce their working set by using run-time handles instead of objects.” 通过存储run-time handles而非Type,MemberInfo object本身可以节约大量内存,然后通过run-time handles转换到对应Type/MemberInfo去访问类型信息。
RuntimeTypeHandle
RuntimeFieldHandle
RuntimeMethodHandle “All of these types are value types that contain just one field, an IntPtr. The IntPtr field is a handle that refers to a type, field, or method in an AppDomain’s loader heap.” Run-time handles只包含一个成员,那就是IntPtr,这里存储的相当于类型信息的索引或指针。而真正的类型信息是存储在AppDomain的Loader heap上。 所以我们只需要通过去构造run-time handles指向AppDomain loader heap上特定type,field,method,然后通过转换handle到对应Type/MemberInfo去访问类型信息就能避免存储大量的Type,MemberInfo对象,从而达到节约内存的目的。 那么我们来看看如何通过run-time handle到底能节约多少内存?如何通过转换run-time handle去访问类型信息:
privatestaticvoidRuntimeTypeHandleAccessObjectTypeInfo() { ShowHeapMemoryUsing("Before do anything!");
List<MethodBase> methodinfos = new List<MethodBase>(); foreach (Type t intypeof(Object).Assembly.GetExportedTypes()) { //skip over any generic types if(t.IsGenericTypeDefinition) continue;
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Methods Number in Object : {0}",methodinfos.Count));
ShowHeapMemoryUsing("After building cache of MethodInfo objects!");
//Build cache of RuntimeMethodHandles for all MethodInfo objects in class.name = classname List<RuntimeMethodHandle> methodhandles = methodinfos.ConvertAll<RuntimeMethodHandle>(mb => mb.MethodHandle);
ShowHeapMemoryUsing("Holding MethodInfo and RuntimeMethodHandle cache!");
//Prevent cache from being GC'd early GC.KeepAlive(methodinfos);
//Allow cache from being GC's now methodinfos = null;
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("objinstance.GetHashCode = {0}",migethashcode.Invoke(objinstance, new Object[]{})));
Note: “The CLR doesn’t support the ability to unload individual assemblies.you want to unload an assembly, you must unload the entire AppDomain that contains it.”(CLR不支持unload单独的assembly,如果需要unload assembly只能通过unload加载了该assembly的AppDomian来实现) “avoid using reflection to access a field or invoke a method property.”( 尽量避免使用反射去调用方法和访问属性成员,因为很慢)
“Serialization is the process of converting an object or a graph of connected objects into a stream of bytes. Deserialization is the process of converting a stream of bytes back into its graph of connected objects.” 序列化和反序列化支持我们把对象信息存储到bytes里,然后通过bytes去构建对象。
“When serializing an object, the full name of the type and the name of the type’s defining assembly are written to the stream.When deserializing an object, the formatter first grabs the assembly identity and ensures that the assembly is loaded into the executing AppDomain by calling System.Reflection.Assembly’s Load method.” 从上面可以看出来,序列化和反序列化的关键技术是通过写入类型信息和类型数据到byte里,然后通过反射实例化出对象。 反序列化的时候一定要确保正确的Assembly被加载,并且类型信息要和序列化时候使用的类型信息对应上。
那么怎么样才是使得类型信息支持序列化了? 我们需要在支持序列化的类型的定义前面加上flag: [Serializable]] “the SerializableAttribute attribute is not inherited by derived types.” 序列化的flag只对父类有效。 既然可以指定可序列化,那么当然也可以指定不支持序列化的flag: [NonSerialized] 那么这些不支持反序列化的成员信息,如何确保在反序列化的时候初始化到正确的值了? 这里就需要一个flag: [OnDeserialized] OnDeserialized标记的方法会在反序列化该类型的时候被调用,用于初始化那些NonSerialized的成员信息。 那么如果我们在将来添加了类型信息里的成员定义,反序列化的时候需要怎样才能保证不出错了? 只需要在新添加的成员定义前添加下面这个flag: [OptionalFieldAttribute] Specifies that a field can be missing from a serialization stream so that the BinaryFormatter and the SoapFormatter does not throw an exception. 标记该成员可以在序列化的时候缺失,不抛出异常。 更多的序列化相关控制标记参见如下: [OnSerializing] – called during serialization of an object [OnSerialized] – called after serialization of an object [OnDeserializing] – called during deserialization of an object [OnDeserialized] – called immediately after deserialization of an object Note: 定义了以上flag的方法必须带一个StreamingContext的参数
The formatter calls FormatterServices’s GetSerializableMembers method. public static MemberInfo[] GetSerializableMembers(Type type, StreamingContext context); 首先获取所有需要Serialize的成员信息(MemberInfo),返回MemberInfo[]
The object being serialized and the array of System.Reflection.MemberInfo objects are then passed to FormatterServices’ static GetObjectData method. 通过MemberInfo去获取Object里成员信息的值,存储在Object[]里
The formatter writes the assembly’s identity and the type’s full name to the stream. 把相关的assembly identity,type名字写入stream
The formatter then enumerates over the elements in the two arrays, writing each member’s name and value to the stream. 最后把所有MemberInfo名字(MemberInfo[]里)和实际Object成员值(Objectp[]里)分别对应写入stream。
更多关于Serialization学习参考《CLR via C#》 – Runtime Serialization章节
Note: The .NET Framework also offers other serialization technologies that are designed more for interoperating between CLR data types and non-CLR data types. (以下serialization技术支持CLR data type和non-CLR data types之间的交互,支持从XML序列化和反序列化,这里暂时没有深入学习了解)
System.Xml.Serialization.XmlSerializer class
System.Runtime.Serialization.DataContractSerializer class 还有一种方式序列化是通过SoapFormatter类,.soap格式。 还有一种高效的平台无关话的序列化反序列化方式,参见Google Protocol Buffer学习 待续……
Platform Invoke
跨语言的调用,比如managed的C#调用unmanaged的C++代码 DllImport – Allow reusing existing unmanaged code in a managed application.
staticvoidMain(string[] args) { #region DLL import Study int a = 1; int b = 2; int sum = 0; sum = MyAdd(a, b); Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0} + {1} = {2}", a, b, sum));
int substractionresult = 0; substractionresult = MySubstract(a, b); Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0} - {1} = {2}", a, b, substractionresult));
// Define a type that will hold any additional information that should be sent to receivers of the event notification internalclassNewMailEventArgs : EventArgs { publicNewMailEventArgs(String from, String to, String subject) { m_From = from; m_To = to; m_Subject = subject; }
public String From{ get { return m_From; } }
privatereadonly String m_From;
public String To { get { return m_To; } }
privatereadonly String m_To;
public String Subject { get { return m_Subject; } }
// Delegate that is used to listen for NewMailEventArgs publicvoidFaxMsg(Object sender, NewMailEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("Faxing mail message:"); Console.WriteLine("From = {0}, To = {1}, Subject = {2}", e.From, e.To, e.Subject); }
// Define a method responsible for raising the event // to notify registered objects that the event has occurred // If this class is sealed, make this method private and nonvirtual // 事件通知 protectedvirtualvoidOnNewMail(NewMailEventArgs e) { // Copy a reference to the delegate field now into a temporary field for thread safety // Be careful race condition EventHandler<NewMailEventArgs> temp = NewMail; // 这里有thread safe问题,但由于delegate is immutable, // 所以我们把NewMail传递给临时变量temp后,无论别人如何改变NewMail都没关系了 // If any methods registered interest with our event, notify them if (temp != null) { temp(this, e); } }
// Define a method that translates the input into the desired event // 事件触发 publicvoidSimulateNewMail(String from, String to, String subject) { // Hold the information we want to pass NewMailEventArgs e = new NewMailEventArgs(from, to, subject);
// Call OnNewMail to notify registered objects that the event has occured OnNewMail(e); } }
测试Event
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
staticvoidMain(string[] args) { EmailManager emailmanager = new EmailManager();
Chars: “In the .NET Framework, characters are always represented in 16-bit Unicode code values, easing the development of global applications.A character is represented with an instance of the System.Char structure (a value type).”
“StringBuilder’s members allow you to manipulate this character array, effectively shrinking the string or changing the characters in the string.”
Unlike a String, a StringBuilder represents a mutable string. This means that most of StringBuilder’s members change the contents in the array of characters and don’t cause new objects to be allocated on the managed heap.”
“String objects referred to by the internal hash table can’t be freed until the AppDomain is unloaded or the process terminates.”
“System.Runtime.CompilerServices.CompilationRelaxations.NoStringInterning flag will control whether to inern all of the string.”
Security String: System.Security.SecureString ……
Note: String object is immutable. The String class is sealed, which means that you cannot use it as a base class for your own type.
Enumerated and Bit Flags
Enum “Every enumerated type is derived directly from System.Enum, which is derived from System.ValueType, which in turn is derived from System.Object” 首先可以看出Enumerated属于Value Type。 这里还是说一下使用Enumerate的好处:
“Enumerated types make the program much easier to write, read, and maintain.”(可视化,容易看懂,无需hard code)
“they’re just a way to associate additional information with a target.The compiler emits this additional information into the managed module’s metadata.” 上面这句话可以理解成,custom attributes是为了关联一些额外的信息到特定的目标上(这里的目标可以是class,event,methods…..),这些额外的信息是被编译器编译保存到了module的metadata里。
using System; [assembly: SomeAttr] // Applied to assembly [module: SomeAttr] // Applied to module [type: SomeAttr] // Applied to type internalsealedclassSomeType<[typevar: SomeAttr] T> { // Applied to generic type variable [field: SomeAttr] // Applied to field public Int32 SomeField = 0; [return: SomeAttr] // Applied to return value [method: SomeAttr] // Applied to method public Int32 SomeMethod( [param: SomeAttr] // Applied to parameter Int32 SomeParam) { return SomeParam; }
[property: SomeAttr] // Applied to property public String SomeProp { [method: SomeAttr] // Applied to get accessor method get { returnnull; } } [event: SomeAttr] // Applied to event [field: SomeAttr] // Applied to compiler-generated field [method: SomeAttr] // Applied to compiler-generated add & remove methods publicevent EventHandler SomeEvent; }
“A custom attribute is simply an instance of a type.” Custom attribute其实也是一个类,只是我们定义custom attribute的时候触发了这些类的构造,把custom attribute的信息写入到了metadata里。
那么知道了Custom attribute是一个类,那么怎么定义Custom attribute了? “Common Language Specification (CLS) compliance, custom attribute classes must be derived, directly or indirectly, from the public abstract System.Attribute class.” 从上面可以看出custom attribute必须直接或间接的继承至System.Attribute class.
namespaceCustomAttrCS { // An enumeration of animals. Start at 1 (0 = uninitialized). publicenum Animal { // Pets. Dog = 1, Cat, Bird, }
// A custom attribute to allow a target to have a pet. // 定义Custom attribute必须直接或间接继承至Attribute publicclassAnimalTypeAttribute : Attribute { // The constructor is called when the attribute is set. // 构建的时候我们可以去设置含参和不含参构造函数 publicAnimalTypeAttribute() { thePet = Animal.Bird; }
// Keep a variable internally ... protected Animal thePet;
// .. and show a copy to the outside world. public Animal Pet { get { return thePet; } set { thePet = Pet; } } }
// A test class where each method has its own pet. classAnimalTypeTestClass { // 定义custom attribute的时候,我们可以调用对应构造函数 [AnimalType(Animals.DOG)] publicvoidDogMethod() { } // 除了调用构造函数外,我们还可以调用Custom Attribute Class的Property设定特定值 [AnimalType(Pet = Animals.CAT)] publicvoidCatMethod() { }
[AnimalType()] publicvoidBirdMethod() { } }
classDemoClass { staticvoidMain(string[] args) { // 通过反射去检查AnimalTypeTestClass里的方法是否定义了Attribute AnimalTypeTestClass testClass = new AnimalTypeTestClass(); Type type = testClass.GetType(); // Iterate through all the methods of the class. foreach(MethodInfo mInfo in type.GetMethods()) { // Iterate through all the Attributes for each method. foreach (Attribute attr in Attribute.GetCustomAttributes(mInfo)) { // Check for the AnimalType attribute. if (attr.GetType() == typeof(AnimalTypeAttribute)) Console.WriteLine( "Method {0} has a pet {1} attribute.", mInfo.Name, ((AnimalTypeAttribute)attr).Pet); }
} } } }
Output: Note: “all non-abstract attributes must contain at least one public constructor.”(非abstract attributes必须至少有一个public构造函数)
知道了Custom Attribute的定义和其限制作用,那么Custom Attribute有什么实际意义了? 还记得在Enumerated Types and Bit Flags讲到的[FLAG]标记改变了Enum.ToString(),Format()行为吗? 正是因为我们动态检查了绑定在Enum上的Flag属性导致的。 而实现动态检查的底层方法是通过reflection(反射 – 参见Hosting,AppDomain,Assembly,Reflection章节) 还记得之前MSDN的例子是如何检查类里各方法是否定义了Attribute吗(这里就是使用了反射)?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
// 通过反射去检查AnimalTypeTestClass里的方法是否定义了Attribute AnimalTypeTestClass testClass = new AnimalTypeTestClass(); Type type = testClass.GetType(); // Iterate through all the methods of the class. foreach(MethodInfo mInfo in type.GetMethods()) { // Iterate through all the Attributes for each method. foreach (Attribute attr in Attribute.GetCustomAttributes(mInfo)) { // Check for the AnimalType attribute. if (attr.GetType() == typeof(AnimalTypeAttribute)) Console.WriteLine( "Method {0} has a pet {1} attribute.", mInfo.Name, ((AnimalTypeAttribute)attr).Pet); } }
“When applying an attribute to a target in source code, the C# compiler allows you to omit the Attribute suffix to reduce programming typing and to improve the readability of the source code.”(注意定义custom attribute的时候,我们可以省略attribute后缀)
“When defining an attribute class’s instance constructor, fields, and properties, you must restrict yourself to a small subset of data types.”(当定义Custom Attribute时,我们只能声明基础类型的fields,properties,constructor(必须符合CLS-compilation))
“Be aware that only Attribute, Type, and MethodInfo classes implement reflection methods that honor the Boolean inherit parameter.”(只有Attribute,Type and MethodInfo实现了反射inherit parameter信息的方法)
Exceptions and State Management
What is Exception? “An expcetion is when a member fails to complete the task it is supposed to perform as indicated by ites name.”
Exception-Handling Mechanics The .NET Framework exception handling mechanism is built using the Structured Exception Handling(SEH) mechanism offered by Windows.
首先看一下捕获异常的最基本写法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
try{ // Put code requiring graceful recovery and/or cleanup operations here... } catch(excetion) { // Put code that recovers from any kind of exception } finally { // Put code that cleans up any operations started within the try block here... // The code in here ALWAYS executes, regardless of whether an exception is thrown. }
Try Block: “A try block contains code that requires common cleanup operations, exception recovery operations, or both.”
Note: “Sometimes developers ask how much code they should put inside a single try block. The answer to this depends on state management.”
Catch Block: “A catch block contains code to execute in response to an exception.”
Note: “When debugging through a catch block by using Microsoft Visual Studio, you can see the currently thrown exception object by adding the special $exception variable name to a watch window.”(当调试catch block的时候,可以通过查看$exception变量名查看异常信息)
Finally Block: “A finally block contains code that’s guaranteed to execute. Typically, the code in a finally block performs the cleanup operations required by actions taken in the try block.”
CLS and Non-CLS Exceptions: CLS(Common Language Specification) – throw Exception-derived objects Non-CLS – throw Exception not derived from Exception
After CLR 2.0: “Microsoft introduced a new RuntimeWrappedException class (defined in the System.Runtime.CompilerServices namespace). This class is derived from Exception, so it is a CLS-compliant exception type. The RuntimeWrappedException class contains a private field of type Object (which can be accessed by using RuntimeWrappedException’s WrappedException read-only property). In CLR 2.0, when a non–CLS-compliant exception is thrown, the CLR automatically constructs an instance of the RuntimeWrappedException class and initializes its private field to refer to the object that was actually thrown.”(CLR 2.0之后,通过RuntimeWrapperdException class把所有的Non-CLS Exception都封装成了CLS Exception)
如果想要就支持2.0之前的行为:
1 2
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices; [assembly:RuntimeCompatibility(WrapNonExceptionThrows = false)]
the stack is really a record of where the thread should return to, not where the thread has come from. (Stack只记录返回点不记录当前点)
The just-in-time (JIT) compiler can inline methods to avoid the overhead of calling and returning from a separate method(JIT编译器使得一些方法称为了inlie的(在当前方法被调用的地方直接展开),从而无法记录到Stack里)
Defining Your Own Exception Class: 自定义Exception类是比较容易出问题且冗长的。 原因如下: “The main reason for this is because all Exception-derived types should be serializable so that they can cross an AppDomain boundary or be written to a log or database”(我们必须保证自定义的Exception类支持序列化,因为我们可能会跨AppDomain去写入Log或则数据库里)
Note: “When you throw an exception, the CLR resets the starting point for the exception; that is, the CLR remembers only the location where the most recent exception object was thrown.”(当我们再次抛出异常的时候,CLR会重置异常,只记录最近异常Object)
Guidelines and Best Practices:
Use finally Blocks Liberally(finlly always execute, do cleanup operations)
Do not Catch Everything
Recovering Gracefully from an Exception(catch some exceptions that are known in advanced and try to recover from it)
Backing Out of a Partially Completed Operation When an Unrecoverble Exception Occus – Maintaining State
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
publicvoidSerializeObjectGraph(FileStream fs, IFormatter formatter, Object rootObj) { // Save the current position of the file. Int64 beforeSerialization = fs.Position; try { // Attempt to serialize the object graph to the file. formatter.Serialize(fs, rootObj); } catch { // Catch any and all exceptions. // If ANYTHING goes wrong, reset the file back to a good state. fs.Position = beforeSerialization; // Truncate the file. fs.SetLength(fs.Position); // NOTE: The preceding code isn't in a finally block because // the stream should be reset only when serialization fails. // Let the caller(s) know what happened by re-throwing the SAME exception. throw; } }
Note:
"After you’ve caught and handled the exception, don’t swallow it—let the caller know that the exception occurred. You do this by re-throwing the same exception."(特别是写给别人用的时候,再次抛出异常让使用者可以去捕获并知道发生了什么)
Hiding an Implementation Detail to Maintain a “Contract” “you might find it useful to catch one exception and re-throw a different exception.”(抛出更符合当前API行为的异常。或则增加更多符合当前API的异常的信息。)
Unhandled Exceptions: 什么时候会出现Unhandled Exceptions? “When an exception is thrown, the CLR climbs up the call stack looking for catch blocks that match the type of the exception object being thrown. If no catch block matches the thrown exception type, an unhandled exception occurs.”(当异常被抛出却没有对应的catch的时候,成为Unhandled Exception) 更多内容参考《CLR via C#》 – Unhandled Exceptions
Note: “When the CLR detects that any thread in the process has had an unhandled exception, the CLR terminates the process.”(当CLR检测到任何线程有未处理的异常的时候,CLR会终止进程)
Debugging Exceptions: VS -> Debug -> Exception 如果针对特定异常勾选抛出,那么当该异常被抛出的会后,程序会进入断点(帮助我们快速定位特定异常)。不勾选也会进入断点(前提是该异常是unhandled)
A Reference Type always goes on the Heap; easy enough, right? (索引类型都是分配在堆上)
Value Types and Pointers always go where they were declared. This is a little more complex and needs a bit more understanding of how the Stack works to figure out where “things” are declared. (值类型和指针是分配在栈上) 下面让我们结合实例来看一下是如何分配在栈和堆上的?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
publicclassMyInt { publicint MyValue; }
public MyInt AddFive(int pValue) { MyInt result = new MyInt(); result.MyValue = pValue + 5; return result; }
当调用AddFive方法的时候,首先函数参数pValue会入栈 然后因为我们创建了索引类型的MyInt实例,这时候MyInt会在堆上分配内存,同时在栈上会生成一个指针指向MyInt在堆上的索引地址 当我们给result.MyValue赋值时,我们通过result Pointer记录的地址去访问堆上的MyValue成员并修改值。 最后我们返回result时,栈被清理,只剩下堆上我们分配的数据。 而剩下堆上的数据,就是由CLR的GC来管理了。 NOTE : “The method does not live on the stack and is illustrated just for reference.” 接下来看看CLR的GC是如何工作的。 在了解GC之前,让我们看看C#里在堆上分配内存是如何分配的? 这里就不得不提new这个关键字了。 当我们通过new去创建reference type的时候,会经历下列步骤:
Calculate the number of bytes required for the type’s fields)(计算type所需分配的内存)
Add the bytes required for an object’s overhead(contain a type object pointer and a sync block index)(为type分配object pointer和sync block index所需内存 – 如果是32-bit Application则分配8 bytes,如果是64-bit Application则分配16 bytes)
Zero out the memory start at NextObjPtr(Indicates where the next object is to be allocated within the heap). Return reference. Move on NextObjPtr to next address that is available to be allocated..(根据NextObjPtr指向的可用堆上的起始位置分配内存并清零,然后传递指向type的内存起始位置的NextObjPtr到构造函数去进行初始化,初始化完成后返回type的索引,最后把NextObjPtr指向下一个heap可分配内存的位置。) 知道了我们在堆上是如何分配内存,让我们看看GC是如何工作来管理所有堆上分配的内存的?
Reference Tracking Algorithm(CLR use. Cares only about reference type variables) 步骤如下:
Marking Phase CLR first suspends all threads in the process(prevents threads from accessing objects and changing their state while the CLR examines them) Marking All objects to 0(means all objects should be deleted) Scan active roots to marking object(not mark the same object again to avoid circular references) 标记阶段,首先悬挂所有线程防止访问Objects和相关状态。 然后标记所有在堆上对象的引用为0,然后扫描所有active的roots(即reference type variables – 引用类型的变量),如果有roots指向任何一个堆上的Object,就标记该Object并对该Object内部的roots进行扫描标记。这里最重要的一点就是对标记过的Object不会再扫描内部root(比如有roots指向了A,我们标记了A,然后检查A内部发现B,因为B还没被标记所以标记B并检查B内部,在B内部又发现了A但因为A已经被标记了,所以不会再次标记A,这样一来如果最初指向A的roots不存在了的话,A和B都会因为没有引用不会被标记而清除。这样一来就避免了Circular references) Note: “Refer to all reference type variables as roots.”
Compacting Phase Shifts the memory consumed by the marked objects down in the heap, compacting all the surviving objects together so that they are contiguous in memory.(reduce application’s working set size &access fast in future & no address space fragmentation issues) CLR resumes all the application’s threads and they continue to access the objects as if the GC never happened at all Note: A static field keeps whatever object it refers to forever or until the AppDomain that the types are loaded into is unloaded 在标记阶段完成后,所有标记为0的堆上对象内存都会被回收。 压缩阶段主要是为了内存的高效利用(防止内存碎片化)。 要注意的是静态变量在内存中的位置不会改变。
接下来看看如何提升GC的performance: CLR’s GC assumptions(提升GC性能的最基本假设): The newer an object is, the shorter its lifetime will be(越新的对象lifetime越短) The older an object is, the longer its lifetime will be(越旧的对象lifetime越长) Collecting a portion of the heap is faster than collecting the whole heap(GC一部分heap比GC所有heap快) 基于上述理论: Heap被分为了Generation 0,1,2。 最初创建的对象会存放在generation 0,GC首先检查Generation 0的对象,objects在通过第一次GC后会提升到generation 1,当generation 1对象数量超过generation 0的时候,GC就会检查generation 0和1,同理当 object从generation 1存活下来后会被存放到generation 2。 通过上述方式,我们GC就不必每次都对整个heap的对象进行检查以达到GC优化的目的。 Note: The Managed heap supports only three generations: generation 0,1,2 The garbage collector fine-tunes itself automatically based on the memory load required by your application. 关于更多GC的学习详情参考《CLR vir C#》 – The Managed Heap and Garbage Collection章节 Note: Finalize methods are called at the completion of a garbage collection on objects that the GC has determined to be garbage.(Object的Finalize方法是在Object在完成内存被回收之前调用) Finalize is not equal to destructor in C++(Finalize!=C++的析构函数)
Threading
What is Thread? “A thread is a Windows concept whose job is to virtualize the CPU. “
Major parts of Thread:
Thread kernel object(“data structes contains a bunch of properties that describe the thread”描述线程信息的数据对象)
Thread environment block(TEB)(“The TEB contains the head of the thread’s exception-handling chain. In addition, the TEB containes the thread’s thread-local storage data and some data structures for use by GDI and OpenGL graphics”)
User-mode stack(“The use-mode stack is used for local variables and arguments passed to methods. It also contains the address indicating what the thread should execute next when the current method returns”)
Kernel-mode stack(“The kernel-mode stack is also used when application code passes arguments to a krenel-mode function in the operating system”)
“LINQ is at the heart of the changes in C# 3. The aim is to make it easy to write queries against multiple data sources with consistent syntax and features, in a readable and composable fashion.”
1 2 3 4
List<Product> products = new List<Product>(); var filtered = from Product p in products where p.Price > 10 select p;
C#4
Named Arguments
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
classProduct { publicstring Name { get { return name; } } readonlystring name;
Unity is a cross-platform game engine developed by Unity Technologies and used to develop video games for PC, consoles, mobile devices and websites. First released on June 8, 2005 (from wiki)
publicclassCameraController : MonoBehaviour { public GameObject m_Player;
private Vector3 m_Offset;
// Use this for initialization voidStart () { m_Offset = transform.position - m_Player.transform.position; } // Update is called once per frame voidLateUpdate () { transform.position = m_Player.transform.position + m_Offset; } }
Rotator.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
using UnityEngine; using System.Collections;
publicclassRotator : MonoBehaviour {
// Use this for initialization voidStart () { } // Update is called once per frame voidUpdate () { transform.Rotate (new Vector3 (15, 35, 45) * Time.deltaTime); } }
// Use this for initialization voidStart () { m_Rigidbody = GetComponent<Rigidbody> (); m_Rigidbody.angularVelocity = Random.insideUnitSphere * m_Tumble; } // Update is called once per frame voidUpdate () { } }
Captures Game Play Win Game
Survival Shooter Game Introduction 固定(2.5D – isometric projection)第三人称视角游戏
Game Introduction Over the course of the project will create procedural tile based levels, implement turn based movement, add a hunger system, audio and mobile touch controls.
publicCount(int min, int max) { minimum = min; maximum = max; } }
publicint columns = 8; publicint rows = 8; public Count wallCount = new Count(5,9); public Count foodCount = new Count(1,5); public GameObject exit; public GameObject[] floorTiles; public GameObject[] wallTiles; public GameObject[] foodTiles; public GameObject[] enemyTiles; public GameObject[] outerwallTiles;
private Transform boardHolder; private List<Vector3> gridPositions = new List<Vector3>();
voidInitialiseList() { gridPositions.Clear ();
for (int x = 1; x < columns - 1; x++) { for(int y = 1; y < rows - 1; y++) { gridPositions.Add(new Vector3(x,y,0f)); } } }
voidBoardSetup() { boardHolder = new GameObject ("Board").transform;
for(int x = -1; x < columns + 1; x++) { for(int y = -1; y < rows + 1; y++) { GameObject toInstantiate = floorTiles[Random.Range (0,floorTiles.Length)]; if(x == -1 || x == columns || y == -1 || y == rows) { toInstantiate = outerwallTiles[Random.Range(0,outerwallTiles.Length)]; }
GameObject instance = Instantiate (toInstantiate, new Vector3(x,y,0f),Quaternion.identity) as GameObject;
using UnityEngine; using System.Collections; using UnityEngine.UI;
publicclassPlayer : MovingObject {
publicint wallDamage = 1; publicint pointsPerFood = 10; publicint pointsPerSoda = 20; publicfloat restartLevelDelay = 1f; public Text foodText;
public AudioClip moveSound1; public AudioClip moveSound2; public AudioClip eatSound1; public AudioClip eatSound2; public AudioClip drinkSound1; public AudioClip drinkSound2; public AudioClip gameOverSound;
Registering The Player Prefab 在Client控制Player Object之前,我们需要去注册该Player Prefab到Network Manager,然后Network Manager会去负责在Server和Client端Spawn Object。 把Player Prefab设置到Network Manager的Player Prefab参数上。 Note: Only the server should create instances of objects which have NetworkIdentity as otherwise they will not be properly connected to the system.(只有server可以创建含NetworkIdentity的实例对象,否则无法正常连接到server system)
Creating Player Movement(Single Player) 在通过server远程执行commands控制Player移动之前,我们先编写简单的控制逻辑用于本地的移动。 挂载PlayerController.cs到Player Prefab上。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
using UnityEngine; using System.Collections;
publicclassPlayerController : MonoBehaviour {
publicfloat mRotateSpeed = 150.0f;
publicfloat mMoveSpeed = 3.0f;
voidUpdate () { var x = Input.GetAxis("Horizontal") * Time.deltaTime * mRotateSpeed; var z = Input.GetAxis("Vertical") * Time.deltaTime * mMoveSpeed;
Testing Multiplayer Movement 再次发布PC版,运行PC版作为Server,Editor版作为Client测试。 这遇到个错误”Spawn scene object not found for 1 UnityEngine.Networking.NetworkIdentity:UNetStaticUpdate()” 根据这里的讨论重新制作Prefab和挂载居然能解决问题,感觉是Unity的bug。 NetworkTransform的一些设定可以控制Network数据同步设定。
Identifying The Local Player 为了显示区分Client和Server的Player对象,我们通过利用NetworkBehaviour的接口方法去修改Local Player的颜色信息。 OnStartLocalPlayer – “Called when the local player object has been set up.”
voidFire() { //Create the bullet from the prefab GameObject bullet = (GameObject)Instantiate(mBulletPrefab, mBulletSpawn.position, mBulletSpawn.rotation);
//Add velocity to the bullet bullet.GetComponent<Rigidbody>().velocity = bullet.transform.forward * mBulletSpeed;
//Destroy the bullet after 2 seconds Destroy(bullet, 2.0f); }
[Command] voidCmdFire() { //Create the bullet from the prefab GameObject bullet = (GameObject)Instantiate(mBulletPrefab, mBulletSpawn.position, mBulletSpawn.rotation);
//Add velocity to the bullet bullet.GetComponent<Rigidbody>().velocity = bullet.transform.forward * mBulletSpeed;
//Spawn the bullet on the clients NetworkServer.Spawn(bullet);
//Destroy the bullet after 2 seconds Destroy(bullet, 2.0f); }
但从上面可以看出只有Server端的血条更新,虽然Client端的值显示变化了但是血条UI却没有变化,这是因为我们指同步了mCurrentHealth数据但没有同步HealthBar Foreground的Rect。
这里需要介绍SyncVar hook. [SyncVar hooks will link a function to the SyncVar. These functions are invoked on the Server and all Clients when the value of the SyncVar changes.](https://unity3d.com/cn/learn/tutorials/topics/multiplayer-networking/networking-player-health?playlist=29690)当SyncVa变化的时候SyncVar Hooks关联的方法会在Server和所有Clients里调用。(用于更新Server和Client的一些相关数据,这里我们是为了更新HealthBar Foreground的Rect)
[OnStartServer is called on the Server when the Server starts listening to the Network](https://unity3d.com/cn/learn/tutorials/topics/multiplayer-networking/handling-non-player-objects?playlist=29690)
OnStartServer在Server端启动的时候调用,这里用来初始化敌人。
在Player Prefab基础上制作EnemyPrefab。

添加EnemyPrefab到NetworkManager的Spawnable List里。
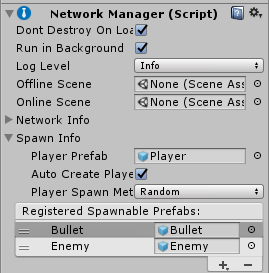
设置EnemySpawner。
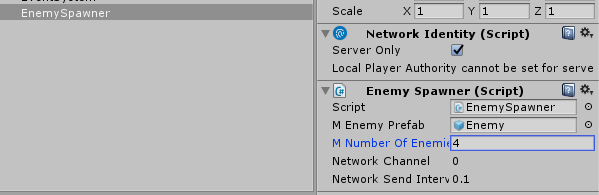
测试效果:
成功创建了Server管理的Enemy。
Spawning And Respawning 随机Spawn到不同的位置。 The NetworkStartPosition component可以用于spawn object到不同的位置。 在场景里创建Gameobject添加NetworkStartPosition并设定位置。 NetworkManager会自动去找到这些带有NetworkStartPosition component的Gameobject,把他们的位置作为Start Position的选项。(Round Robin Player Spawn Method on the Network Manager) Spawn和Respawn等内容详情参考Spawning and Respawning Multiplayer Networking教程学习终于结束了。但初次接触Unity Networking的学习,还有很多地方理解错误的地方,欢迎纠正。
C# runtime performance still lags behind C/C++(C#运行效率没有C/C++好)
Latest and greatest .NET language and runtime features are not supported in Unity’s current version of Mono.(新版本的.Net语言和运行时特性没有被当前的Unity版本支持)
With around 23 platforms and architecture permutations, a large amount of effort is required for porting, maintaining, and offering feature and quality parity.(Mono VM在跨平台的维护上很费时费力)
Garbage collection can cause pauses while running(Mono VM现有的GC很容易使得游戏卡顿)
Performance(效率上的优化),原因如下 . C++ compilers and linkers provide a vast array of advanced optimisations previously unavailable. . Static analysis is performed on your code for optimisation of both size and speed. . Unity-focused optimisations to the scripting runtime.
All code generation is done to C++ rather than architecture specific machine code. The cost of porting and maintenance of architecture specific code generation is now more amortised. (因为现在是通过利用现有的C++编译器编译C++而没有直接编译成特定架构的机器代码,这样一来跨平台的移植和维护责任就更分散了)
Feature development and bug fixing proceed much faster. For us, days of mucking in architecture specific files are replaced by minutes of changing C++. Features and bug fixes are immediately available for all platforms. (功能开发和bug修改更容易快捷。通过修改IL2CPP的C++生成就能快速的针对多个平台有效)
IL2CPP is not tied to any one specific garbage collector, instead interacting with a pluggable API(GC导致游戏卡顿的现象也可以通过不同的GC方式来改善)
Value types as Dictionary Keys 值类型作为Dictionary的Key时会有问题,实际上实现了IEquatable的类型都会有此问题,因为Dictionary的默认构造函数会使用EqualityComparer.Default作为比较器,而对于实现了IEquatable的类型,EqualityComparer.Default要通过反射来实例化一个实现了IEqualityComparer的类(可以参考EqualityComparer的实现)。 解决方案是自己实现一个IEqualityComparer,然后使用Dictionary<TKey, TValue>(IEqualityComparer)构造器创建Dictionary实例。 讲到如果T实现了IEquatable,那么就会反射实例化一个实现了IEqualityCompareer的类,这里通过查看EqaulityCompare源码可以看到确实如此。
RuntimeType t = (RuntimeType)typeof(T); // Specialize type byte for performance reasons if (t == typeof(byte)) { return (EqualityComparer<t>)(object)(new ByteEqualityComparer()); } // If T implements IEquatable<t> return a GenericEqualityComparer<t> if (typeof(IEquatable<t>).IsAssignableFrom(t)) { //return (EqualityComparer<t>)Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(GenericEqualityComparer<>).MakeGenericType(t)); return (EqualityComparer<t>)RuntimeTypeHandle.CreateInstanceForAnotherGenericParameter((RuntimeType)typeof(GenericEqualityComparer<int>), t); } // If T is a Nullable<u> where U implements IEquatable<u> return a NullableEqualityComparer<u> if (t.IsGenericType && t.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(Nullable<>)) { RuntimeType u = (RuntimeType)t.GetGenericArguments()[0]; if (typeof(IEquatable<>).MakeGenericType(u).IsAssignableFrom(u)) { //return (EqualityComparer<t>)Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(NullableEqualityComparer<>).MakeGenericType(u)); return (EqualityComparer<t>)RuntimeTypeHandle.CreateInstanceForAnotherGenericParameter((RuntimeType)typeof(NullableEqualityComparer<int>), u); } } // If T is an int-based Enum, return an EnumEqualityComparer<t> // If you update this check, you need to update the METHOD__JIT_HELPERS__UNSAFE_ENUM_CAST case in getILIntrinsicImplementation if (t.IsEnum && Enum.GetUnderlyingType(t) == typeof(int)) { return (EqualityComparer<t>)RuntimeTypeHandle.CreateInstanceForAnotherGenericParameter((RuntimeType)typeof(EnumEqualityComparer<int>), t); } // Otherwise return an ObjectEqualityComparer<t> returnnew ObjectEqualityComparer<t>(); }
...... }
注意下面这个分支
1 2 3 4 5
// If T implements IEquatable<t> return a GenericEqualityComparer<t> if (typeof(IEquatable<t>).IsAssignableFrom(t)) { //return (EqualityComparer<t>)Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(GenericEqualityComparer<>).MakeGenericType(t)); return (EqualityComparer<t>)RuntimeTypeHandle.CreateInstanceForAnotherGenericParameter((RuntimeType)typeof(GenericEqualityComparer<int>), t); }
当我们的的T也就是我们的Dictionary<TKey,TValue>里面的TKey实现了IEquatable<T>接口的话,里面的代码实现看不太懂,大概是动态创建实现了IEqualityComparer<TKey>的类,然后实例化返回了一个作为TKey的EqualityComparer。
"This works for reference types (as the reflection+create a new type step is skipped)"
当我们传递的TKey是reference types的时候不会触发创建实现了IEqualityCompareer<TKey>的类,直接返回ObjectEqualityComparer<t>()。
解决方案:
如果我们一定要在IOS上把value type作为Dictionary的Key的话,我们需要自己实现一个实现了IEqualityCompareer<TKey>的类,然后作为TKey的EqualityComparer传递给Dictionary<TKey,TVlue>的构造函数。
比如我们要给int添加我们自己的比较方法,那么按如下方式写即可。
publicclassValueTypeComparer : EqualityComparer<int> { publicoverrideboolEquals(int a, int b) { Console.WriteLine("ValueTypeComparer:Equals() called"); if (a == b) { returntrue; } else { returnfalse; } }
publicoverrideintGetHashCode(int a) { Console.WriteLine("ValueTypeComparer:GetHashCode() called"); return a.GetHashCode(); } }
classProgram { staticvoidMain(string[] args) { ValueTypeComparer valuetypecomparer = new ValueTypeComparer(); int vt1 = 1; Dictionary<int, bool> mydictionary1 = new Dictionary<int, bool>(valuetypecomparer); mydictionary1.Add(vt1, true); mydictionary1.ContainsKey(vt1); } }
AssemblyName aname = new AssemblyName("DynamicgAssembly"); AssemblyBuilder ab = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.DefineDynamicAssembly(aname, AssemblyBuilderAccess.RunAndSave);
Note: IOS只支持static code, Unlike traditional Mono/.NET, code on the iPhone is statically compiled ahead of time instead of being compiled on demand by a JIT compiler(IOS只支持full aot,不支持JIT).所以有些动态特性没法被Full AOT支持。 But the entire Reflection API, including Type.GetType (“someClass”), listing methods, listing properties, fetching attributes and values works just fine.(反射依然在IOS可用)
#if UNITY_IPHONE || UNITY_XBOX360 //On iOS and Xbox 360 plugins are statically linked into //the executable, so we have to use **Internal as the //library name. [DllImport ("**Internal")] #else // Other platforms load plugins dynamically, so pass the name // of the plugin's dynamic library. [DllImport ("PluginName")] #endif
Screen coordinates Is 2D, measured in pixels and start in the lower left corner at (0,0) and go to (Screen.width, Screen.height). Screen coordinates change with the resolution of the device, and even the orientation (if you app allows it) on mobile devices. 左下角为(0,0),右上角为(Screen.width, Screen.height)
GUI coordinates Is used by the GUI system. They are identical to Screen coordinates except that they start at (0,0) in the upper left and go to (Screen.width, Screen.height) in the lower right. 左上角为(0,0),右下角为(Screen.width, Screen.height)
Viewport coordinates Is the same no matter what the resolution. The are 2D, start at (0,0) in the lower left and go to (1,1) in the upper right. For example (0.5, 0.5) in viewport coordinates will be the center of the screen no matter what resolution or orientation. 相对于摄像机坐标系而言的,近平面(0,0),远平面(1,1),(0.5,0.5)表示在摄像机坐标系的中间。
World coordinates Is a 3D coordinates system and where all of your object live. 世界坐标系的(x,y,z)
Unity Unit & Pixel Per Unit
Unity Unit Unity Unit代表Unity里的一个Unit单位代表物理大小,默认是1 unit = 1 meter 所以我们在建模的时候如果想导入到Unity后保持scale(1,1,1)就应该把建模软件也设定成1 unit = 1 meter。 Unity Unit主要影响的是Physical(比如重力加速度的运算,如果修改Unit为厘米,但不重新计算重力加速度,那么物体会落的很快)
Pixel Per Unit Pixel Per Unit主要影响Sprite在屏幕上的映射显示。表示多少个像素等价于一个Unit,后面会详细讲到。
Vector2 screenSize = new Vector2(Screen.width, Screen.height); float scaleFactor = 0; switch (m_ScreenMatchMode) { case ScreenMatchMode.MatchWidthOrHeight: { // We take the log of the relative width and height before taking the average. // Then we transform it back in the original space. // the reason to transform in and out of logarithmic space is to have better behavior. // If one axis has twice resolution and the other has half, it should even out if widthOrHeight value is at 0.5. // In normal space the average would be (0.5 + 2) / 2 = 1.25 // In logarithmic space the average is (-1 + 1) / 2 = 0 float logWidth = Mathf.Log(screenSize.x / m_ReferenceResolution.x, kLogBase); float logHeight = Mathf.Log(screenSize.y / m_ReferenceResolution.y, kLogBase); float logWeightedAverage = Mathf.Lerp(logWidth, logHeight, m_MatchWidthOrHeight); scaleFactor = Mathf.Pow(kLogBase, logWeightedAverage); break; } case ScreenMatchMode.Expand: { scaleFactor = Mathf.Min(screenSize.x / m_ReferenceResolution.x, screenSize.y / m_ReferenceResolution.y); break; } case ScreenMatchMode.Shrink: { scaleFactor = Mathf.Max(screenSize.x / m_ReferenceResolution.x, screenSize.y / m_ReferenceResolution.y); break; } }
// Reading from a excel file IExcelDataReader excelreader = ExcelReaderFactory.CreateOpenXmlReader(stream);
// DataSet -- the result of each spreadsheet will be created in the result tables DataSet result = excelreader.AsDataSet();
int sheetcount = result.Tables.Count; Debug.Log("sheetcount = " + sheetcount);
for(int m = 0; m < sheetcount; m++) { int rows = result.Tables[m].Rows.Count; int columns = result.Tables[m].Columns.Count; Debug.Log(string.Format("Table[{0}] with row = {1} columns = {2}", m, rows, columns));
serialization is the process of converting the state an object to a set of bytes in order to store (or transmit) the object into memory, a database or a file.
Writing routines that have to wait for another operation to complete
What is a coroutine?
Coroutines are not threads and coroutines are not asynchronous.
A coroutine is a function that is executed partially and, presuming suitable conditions are met, will be resumed at some point in the future until its work is done. The start of a coroutine corresponds to the creation of an object of type coroutine. That object is tied to the MonoBehaviour component that hosted the call.
How long is the life cycle? & When does coroutine get called?
The lifetime of the Coroutine object is bound to the lifetime of the MonoBehaviour object, so if the latter gets destroyed during process, the coroutine object is also destroyed. Whenever game object that is bound to coroutine is destroyed or inactive(e.g. gameobject.SetActive(false), Destroy(gameobject)), the coroutine will stop to be called. Coroutine is run until a yield is found.
IEnumerator LateCoutine() { Debug.Log("This is Late Coroutine Call Before"); yieldreturnnull; Debug.Log("This is Late Coroutine Call After"); }
private IEnumerator CoroutineCall() { for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) { mCoroutineText = i.ToString(); Debug.Log("Coroutine Text: " + mCoroutineText); yieldreturnnewWaitForSeconds(1.0f); } mCoroutineText = "Finished"; } }
ScreenShots
Note: Diable Monobehaviour(e.g. Monobehaviour.enabled = false) will not influence coroutine.
Coroutine with yiled return null will get called after LateUpdate()(仅根据上面的测试结果) 通过返回WaitForSeconds() || WaitForEndOfFrame() || WaitForFixedUpdate() 等yield return 支持的返回类型可以实现coroutine在特定时刻继续调用
List<System.Collections.IEnumerator> m_Enumerators = new List<System.Collections.IEnumerator>();
List<System.Collections.IEnumerator> m_EnumeratorsBuffer = new List<System.Collections.IEnumerator>();
voidAwake() { if (Instance == null) { Instance = this; } else { Debug.Log ("Multi-instances of CouroutineManager"); } }
voidLateUpdate() { for (int i = 0; i < m_Enumerators.Count; i++) { //handle special enumerator if(m_Enumerators[i].Current is CoroutineYieldInstruction) { CoroutineYieldInstruction yiledinstruction = m_Enumerators[i] .Current as CoroutineYieldInstruction; if(!yiledinstruction.IsDone()){ continue; } }
//Do normal move next if(!m_Enumerators[i].MoveNext()){ m_EnumeratorsBuffer.Add(m_Enumerators[i]); continue; } }
//remove end enumerator for(int i = 0; i < m_EnumeratorsBuffer.Count; i++) { m_Enumerators.Remove(m_EnumeratorsBuffer[i]); }
using UnityEngine; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic;
publicclassForEachAndFor : MonoBehaviour {
private List<int> mTestList;
// Use this for initialization voidStart () { mTestList = new List<int>(1000); for(int i = 0; i < mTestList.Count; i++) { mTestList[i] = i; } } // Update is called once per frame voidUpdate () { foreach(var it in mTestList) {
} /* for(int i = 0; i < mTestList.Count; i++) { } */ } }
privatevoidStart() { this.mTestList = new List<int>(1000); for (int i = 0; i < this.mTestList.get_Count(); i++) { this.mTestList.set_Item(i, i); } }
privatevoidUpdate() { using (List<int>.Enumerator enumerator = this.mTestList.GetEnumerator()) { while (enumerator.MoveNext()) { int current = enumerator.get_Current(); } } } }
一下学习参考: Shuffle Bags: Making Random() Feel More Random Never-ending Shuffled Sequences - When Random is too Random 实现参考: Shuffle bag algorithm implemented in C# 那么什么是Shuffle Bag了? “ A Shuffle Bag is a technique for controlling randomness to create the distribution we desire. The idea is: Pick a range of values with the desired distribution. Put all these values into a bag. Shuffle the bag’s contents. Pull the values out one by one until you reach the end. Once you reach the end, you start over, pulling the values out one by one again. “ 从上面可以看出Shuffle Bag主要是通过把所有可能都放到List里,然后通过随机选择在里面选取一个,而被选择过的不记入下一次选择考虑范围内,直到List里所有可能都被选择完为止。 这样一来List里填充的数据就确定了每一个事件发生的概率。 并且只通过一次填充数据就能无限随机选择下去。
//If any child is bigger than parent, //then we swap it and do adjust for child again to make sure meet max heap definition if( max_index != parentindex ) { swap_time++; swap(sortarray[max_index], sortarray[parentindex]); heapAdjust(sortarray, max_index, length); } }
//通过初试数据构建最大堆 voidbuildingHeap(int* sortarray) { for( int i = int(intArraySize(sortarray)/2) - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //1.2 Adjust heap //Make sure meet max heap definition //Max Heap definition: // (k(i) >= k(2i) && k(i) >= k(2i+1)) (1 <= i <= n/2) heapAdjust(sortarray, i, intArraySize(sortarray)); } }
//1. Build max heap // 1.1 Init heap //Assume we construct max heap buildingHeap(sortarray); //2. Sort heap //这里花O(n),跟数据数量有关 for( int i = intArraySize(sortarray) - 1; i > 0; i-- ) { //swap first element and last element //do adjust heap process again to make sure the new array are still max heap swap(sortarray[i],sortarray[0]); //Due to we already building max heap before, //so we just need to adjust for index 0 after we swap first and last element heapAdjust(sortarray, 0, i); } }
intpartition(int* sortarray, int l, int r) { //choose pivot int pivot = sortarray[r]; int i = l; for( int j = l; j < r; j++ ) { time_complexity++; if( sortarray[j] <= pivot ) { swap(sortarray[i],sortarray[j]); i++; } } swap(sortarray[i], sortarray[r]); return i; }
voidquicksort(int* sortarray, int low, int high, bool benableoptimize) { //partition //Here we use last element of array as pivot //recursion //Pivot chosen to optimize quicksort // median-of-three int pivotpos; int middlepos = (high + 1) / 2; if( benableoptimize ) { if( sortarray[low] > sortarray[middlepos] ) { swap(sortarray[low],sortarray[middlepos]); }
voidmerge(vector& sortarray, int start, int middle, int end) { int left_size = middle - start + 1; int right_size = end - middle; vector left; vector right; for( int i = 0; i < left_size; i++ ) { left.push_back(sortarray[start + i]); }
int k = 0; int l = 0; int index = start; //The worst condition is compare n * log(n) - n + 1 //The best condition is compare n * log(n) / 2 while( k < left_size && l < right_size ) { if( left[k] < right[l] ) { sortarray[index] = left[k]; k++; } else { sortarray[index] = right[l]; l++; } index++; }